Hey everyone,
If you're a Linux user who spends any amount of time in the terminal, you've probably heard the news: the incredibly popular system information tool, neofetch, has been archived and is no longer being actively maintained.
Now, the community has plenty of fantastic alternatives, with fastfetch being one of my personal favorites. But you know me... why just use someone else's tool when you can write your own and learn some stuff in the process?
So, in that spirit, I wanted to share not one, but two simple "fetch" utilities I've put together: one in pure Bash, and a more feature-rich version in Python.
1. fetch_pretty.sh - The Lightweight Bash Version
First up is a simple script written entirely in Bash. It doesn't have a million features, but it's lightweight and does the basics: it grabs your OS, kernel version, current shell, and desktop environment/window manager, then prints it out with a splash of color. It's a great example of how much you can do with just standard shell commands.
The Output:

The Code (fetch_pretty.sh):
#!/bin/bash
# Get the operating system name and version
os=$(lsb_release -ds)
# Get the kernel version
kv=$(uname -r)
# Get the name of the current shell
sh=${SHELL##*/}
# Initialize the user interface variable to 'unknown'
ui='unknown'
# Determine the user interface (desktop environment or window manager)
if [ -n "${DE}" ]; then
ui="${DE}" # If DE variable is set, use it
elif [ -n "${WM}" ]; then
ui="${WM}" # If WM variable is set, use it
elif [ -n "${XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP}" ]; then
ui="${XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP}" # Use XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP if set
elif [ -n "${DESKTOP_SESSION}" ]; then
ui="${DESKTOP_SESSION}" # Use DESKTOP_SESSION if set
elif [ -n "${rcwm}" ]; then
ui="${rcwm}" # Use rcwm if set
elif [ -n "${XDG_SESSION_TYPE}" ]; then
ui="${XDG_SESSION_TYPE}" # Use XDG_SESSION_TYPE if set
fi
# Get the base name of the user interface variable
ui="$(basename "${ui}")"
# Function to set text color based on input argument
color() {
case "$1" in
red) printf '\033[1;31m' ;; # Set color to red
green) printf '\033[1;32m' ;; # Set color to green
yellow) printf '\033[1;33m' ;; # Set color to yellow
blue) printf '\033[1;34m' ;; # Set color to blue
magenta) printf '\033[1;35m' ;; # Set color to magenta
cyan) printf '\033[1;36m' ;; # Set color to cyan
gray) printf '\033[1;30m' ;; # Set color to gray
white) printf '\033[1;37m' ;; # Set color to white
reset) printf '\033[0m' ;; # Reset color to default
esac
}
# Initialize output variable with a newline
output="\n"
# Append formatted OS information to output
output+=$(printf "%b" "$(color red) os - $(color reset)$os\n")"\n"
# Append formatted kernel version to output
output+=$(printf "%b" "$(color yellow) kr - $(color reset)$kv\n")"\n"
# Append formatted shell information to output
output+=$(printf "%b" "$(color green) sh - $(color reset)$sh\n")"\n"
# Append formatted window manager information to output
output+=$(printf "%b" "$(color blue) wm - $(color reset)$ui\n")"\n\n"
# Convert output to lowercase efficiently
output=$(tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' <<< "$output")
# Print the final output
printf "%b" "$output"
# Print a modern, colorful bar using solid block characters (optimized)
for color in red green yellow blue magenta cyan gray white; do
printf "%s\u2588\u2588 %s" "$(color "$color")" "$(color reset)"
done
printf "\n"
2. pyfetch.py - The "Richer" Python Version
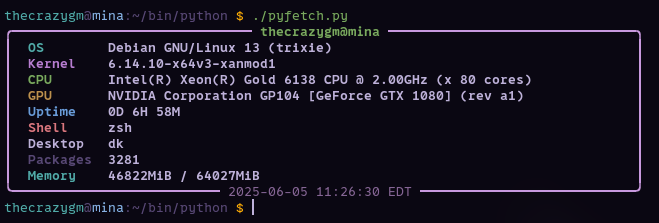
Next, I decided to build a more comprehensive version in Python, leveraging the amazing rich library to create a nicely formatted panel. This one digs a bit deeper, fetching more information like CPU/GPU models, memory usage, uptime, and even package counts for various systems (Debian, Arch, and RPM-based distros).
The end result is a clean, modern-looking info panel right in your terminal.
The Output:
The Code (pyfetch.py):
#!/usr/bin/env -S uv run --quiet --script
# /// script
# requires-python = ">=3.13"
# dependencies = [
# "rich",
# ]
#
# ///
"""
A pretty system fetch utility inspired by fetch.sh and fetch_pretty.sh, using the rich library for output.
"""
import os
import platform
import socket
import subprocess
from datetime import timedelta
from datetime import datetime
from rich.console import Console
from rich.panel import Panel
from rich.table import Table
from rich.text import Text
console = Console()
def get_os(): #
try:
if os.path.exists("/etc/os-release"):
with open("/etc/os-release") as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("PRETTY_NAME="):
return line.strip().split("=", 1)[1].strip('"')
return platform.system()
except Exception:
return platform.system()
def get_kernel(): #
return platform.release()
def get_user_host(): #
return f"{os.getenv('USER') or os.getenv('LOGNAME')}@{socket.gethostname()}"
def get_uptime(): #
try:
with open("/proc/uptime") as f:
uptime_seconds = float(f.readline().split()[0])
uptime_td = timedelta(seconds=int(uptime_seconds))
days = uptime_td.days
hours, remainder = divmod(uptime_td.seconds, 3600)
minutes, _ = divmod(remainder, 60)
return f"{days}D {hours}H {minutes}M"
except Exception:
return "Unknown"
def get_shell(): #
return os.path.basename(os.getenv("SHELL", "Unknown"))
def get_desktop(): #
# Try common environment variables
for var in [
"XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP",
"DESKTOP_SESSION",
"DE",
"WM",
"XDG_SESSION_TYPE",
]:
val = os.getenv(var)
if val:
return val
# Try to detect from running processes
try:
for pid in os.listdir("/proc"):
if pid.isdigit():
try:
with open(f"/proc/{pid}/comm") as f:
proc = f.read().strip()
if any(
wm in proc.lower()
for wm in [
"awesome",
"xmonad",
"qtile",
"sway",
"i3",
"openbox",
"fluxbox",
"bspwm",
"wm",
]
):
return proc
except Exception:
continue
except Exception:
pass
return "Unknown"
def get_package_count(): #
# Try dpkg (Debian/Ubuntu)
try:
result = subprocess.run(["dpkg", "-l"], capture_output=True, text=True)
count = sum(1 for line in result.stdout.splitlines() if line.startswith("ii"))
return str(count)
except Exception:
pass
# Try rpm (Fedora/openSUSE/RHEL)
try:
result = subprocess.run(["rpm", "-qa"], capture_output=True, text=True)
count = len(result.stdout.splitlines())
return str(count)
except Exception:
pass
# Try pacman (Arch/Manjaro/Artix)
try:
result = subprocess.run(["pacman", "-Q"], capture_output=True, text=True)
count = len(result.stdout.splitlines())
return str(count)
except Exception:
pass
return "N/A"
def get_memory(): #
try:
with open("/proc/meminfo") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
mem_total = (
int([line for line in lines if line.startswith("MemTotal:")][0].split()[1])
// 1024
)
mem_free = (
int(
[line for line in lines if line.startswith("MemAvailable:")][0].split()[
1
]
)
// 1024
)
return f"{mem_free}MiB / {mem_total}MiB"
except Exception:
return "Unknown"
def get_cpu(): #
model = None
cores = 0
try:
with open("/proc/cpuinfo") as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("model name") and model is None:
model = line.strip().split(":", 1)[1].strip()
if line.startswith("processor"):
cores += 1
if model and cores:
return f"{model} (x {cores} cores)"
elif model:
return model
else:
return platform.processor() or "Unknown"
except Exception:
return "Unknown"
def get_gpu(): #
try:
result = subprocess.run(["lspci"], capture_output=True, text=True)
gpus = []
for line in result.stdout.splitlines():
if any(
x in line.lower()
for x in ["vga compatible controller", "3d controller"]
):
# Get the part after the last colon (the model)
if ":" in line:
gpu_model = line.split(":")[-1].strip()
gpus.append(gpu_model)
if gpus:
return "; ".join(gpus)
else:
return "Unknown"
except Exception:
return "Unknown"
def main():
info = {
"OS": get_os(),
"Kernel": get_kernel(),
"CPU": get_cpu(),
"GPU": get_gpu(),
"Uptime": get_uptime(),
"Shell": get_shell(),
"Desktop": get_desktop(),
"Packages": get_package_count(),
"Memory": get_memory(),
}
table = Table(show_header=False, show_edge=False, box=None, padding=(0, 1))
colors = [
"cyan",
"magenta",
"green",
"yellow",
"blue",
"red",
"white",
"bright_black",
]
for idx, (k, v) in enumerate(info.items()):
label = Text(f"{k}", style=f"bold {colors[idx % len(colors)]}")
value = Text(v, style="bold white")
table.add_row(label, value)
# Use the current local time
current_time = datetime.now().astimezone()
formatted_time = current_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %Z")
panel = Panel(
table,
title=f"[bold green]{get_user_host()}[/bold green]",
border_style="bright_magenta",
padding=(0, 1),
width=80,
subtitle=f"[dim]{formatted_time}[/dim]",
)
console.print(panel)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
It was a fun little project to see what I could pull together. As I've said before, reinventing the wheel is one of the best ways to learn the ins and outs of your system and the tools you use.
As always,
Michael Garcia a.k.a. TheCrazyGM



