
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

07-05-2025 - Physics - Magnetism and current [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_30-29-28)
Magnetism and current

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
*Effect of a magnetic field on an electric current
Sometimes the most important things that happen in our world are invisible and are gifts of nature, such as gravitational force. We remain attached to the earth precisely thanks to gravitational force. There is another thing that our world gives us every day and that is the effect of magnetism on electric current.
The effect of magnetism on electric current is the basis of many fundamental phenomena in electrical engineering and physics.
So what is the effect of a magnetic field on an electric current?
The magnetic field generates a force on an electric current, or better yet, a magnetic field exerts a force on an electric current that passes through a conductor.
Laplace's second law
There is something already studied that unites the two concepts of magnetic induction field and electric current. We are talking about Laplace's second law.
Below I show the mathematical description of Laplace's second law:
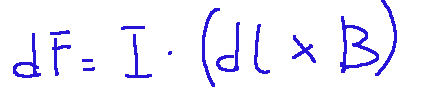
Where:
dF = infinitesimal force exerted on the wire
I = intensity of the electric current (Ampere)
dL = infinitesimal element of length of the conductor
B = vector of the magnetic field (Tesla)
x = vector product
This law contains the fundamental principle used to generate motion in electric motors.
The magnetic moment
The magnetic moment is expressed mathematically as follows:
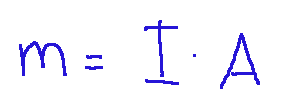
Where:
m = magnetic moment vector (Ampere m²)
I = intensity of the electric current (Ampere),
A = area of the conducting loop (m²)
The magnetic moment is used to describe the intensity and orientation of a magnetic system.
There can be different magnetic moments:
-Orbital magnetic moment
-Spin magnetic moment
-Magnetic moment of the loops
Laplace's first law
Laplace's first law explains the interaction between an electric current and a magnetic field. Since these interactions are so many in our world, this law is considered important. Furthermore, this law is also known as the law of magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor.
This law technically states the following:
A straight conductor carrying current and immersed in a uniform magnetic field experiences a force proportional to the intensity of the current, the length of the conductor, and the intensity of the magnetic field.
Here is the formula:
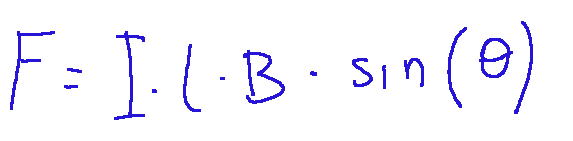
Where:
F = magnetic force (Newton)
I = intensity of the current (Ampere)
l = length of the conductor (meters)
B = intensity of the magnetic field (Tesla)
θ = angle between the conductor and the magnetic field lines
Ampere's Theorem
When we are in the field of electromagnetism, another of the fundamental principles is Ampere's Theorem.
This theorem states that:
The sum of the magnetic field intensities along a closed path is proportional to the total electric current that passes through the surface enclosed by the path.
The theorem is expressed mathematically as follows:
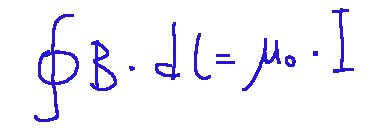
Where:
B = magnetic field vector (Tesla)
dl = infinitesimal element of the closed path
μ0 = magnetic permeability of vacuum
I = total electric current that passes through the surface delimited by the path
The meaning of the formula described above is that the magnetic field generated by a current depends only on the amount of current that passes through the surface enclosed by the path.
Conclusions
The study of magnetism and electric current is fundamental from a scientific point of view, but it was and is crucial from a technological point of view. Domestic electricity, motors and generators are technological applications that come from studies on electromagnetism.
Question
Laplace's theory was experimentally defined as correct by Ørsted only in 1820. Did you know that Laplace (1749-1827) hypothesized that electric current produced magnetic effects before this was discovered experimentally?

ITALIAN

07-05-2025 - Fisica - Magnetismo e corrente [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_30-29-28)
Magnetismo e corrente

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
*Effetto di un campo magnetico su una corrente elettrica
A volte le cose più importanti che avvengono nel nostro mondo sono invisibili e sono regali della natura, come la forza gravitazionale. Noi rimaniamo attaccati alla terra proprio grazie alla forza gravitazionale. C’è un altra cosa che il nostro mondo ci regala ogni giorno ed è l’effetto del magnetismo sulla corrente elettrica.
L’effetto del magnetismo sulla corrente elettrica è alla base di molti fenomeni fondamentali dell’elettrotecnica e della fisica.
Quindi qual è l'effetto di un campo magnetico su una corrente elettrica?
Il campo magnetico genera una forza su una corrente elettrica, o meglio ancora, un campo magnetico esercita una forza su una corrente elettrica che attraversa un conduttore.
La seconda legge di Laplace
C’è qualcosa di già studiato che unisce i due concetti di campo di induzione magnetica alla corrente elettrica. Stiamo parlando della seconda legge di Laplace.
Qui di seguito mostro la descrizione matematica della seconda legge di Laplace:
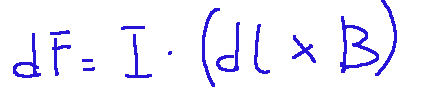
Dove:
dF = forza infinitesimale esercitata sul filo
I = intensità della corrente elettrica (Ampere)
dL = elemento infinitesimale di lunghezza del conduttore
B = vettore del campo magnetico (Tesla)
x = prodotto vettoriale
Questa legge contiene il principio fondamentale usato oer generare movimento nei motori elettrici.
Il momento magnetico
Il momento magnetico si esprime matematicamente così:
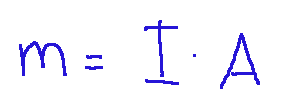
Dove:
m = vettore momento magnetico (Ampere·m²)
I = intensità della corrente elettrica (Ampere),
A = area della spira conduttrice (m²)
Il momento magnetico viene usato per descrivere l’intensità e l’orientamento di un sistema magnetico.
I momenti magnetici possono essere diversi:
-Momento magnetico orbitale
-Momento magnetico di spin
-Momento magnetico delle spire
La prima legge di Laplace
La prima legge di Laplace spiega l’interazione tra una corrente elettrica e un campo magnetico. Siccome queste interazioni sono davvero tante nel nostro mondo, questa legge è ritenuta importante. Inoltre questa legge è conosciuta anche come legge della forza magnetica su un conduttore percorso da corrente.
Questa legge tecnicamente afferma quanto segue:
Un conduttore rettilineo percorso da corrente e immerso in un campo magnetico uniforme subisce una forza proporzionale all'intensità della corrente, alla lunghezza del conduttore e all'intensità del campo magnetico.
Qui di seguito la formula:
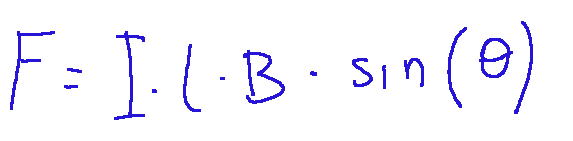
Dove:
F = forza magnetica (Newton)
I = intensità della corrente (Ampere)
l = lunghezza del conduttore (metri)
B = intensità del campo magnetico (Tesla)
θ = angolo tra il conduttore e le linee del campo magnetico
Il Teorema di Ampere
Quando siamo nel campo dell’elettromagnetismo, un altro dei principi fondamentali è il Teorema di Ampere.
Questo teorema dice che:
La somma delle intensità del campo magnetico lungo un percorso chiuso è proporzionale alla corrente elettrica totale che attraversa la superficie racchiusa dal percorso.
Il teorema si esprime matematicamente come segue:
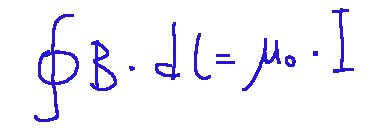
Dove:
B = vettore del campo magnetico (Tesla)
dl = elemento infinitesimo del percorso chiuso
μ0 = permeabilità magnetica del vuoto
I = corrente elettrica totale che attraversa la superficie delimitata dal percorso
Il significato della formula descritta prima è che il campo magnetico generato da una corrente dipende solo dalla quantità di corrente che attraversa la superficie racchiusa dal percorso.
Conclusioni
Lo studio del magnetismo e della corrente elettrica è fondamentale dal punto di vista scientifico, ma è stato ed è cruciale dal punto di vista tecnologico. L'elettricità domestica, i motori e i generatori, sono applicazioni tecnologiche che arrivano dagli studi sull'elettromagnetismo.
Domanda
La teoria di Laplace fu definita corretta in maniera sperimentale da Ørsted solo nel 1820. Lo sapevate che Laplace (1749-1827) ipotizzò che la corrente elettrica producesse effetti magnetici prima che questo venisse scoperto sperimentalmente?
THE END


