~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
07-02-2024 - Physics - Energy exchange in a wall-tent system [EN]-[IT]
Energy exchange in a wall-tent system
Basic concepts
Thermodynamic transformations
To understand thermodynamic transformations we can start from the postulate that, in a constant mass system, the entropy flow is linked only to the heat flow.
we can translate this with the following formula
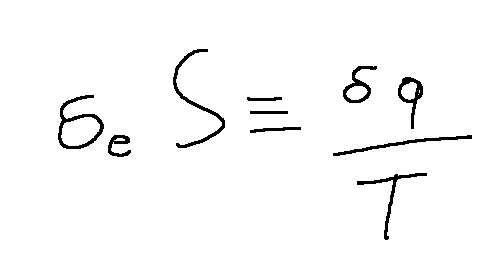
From which we can obtain the entropy balance:
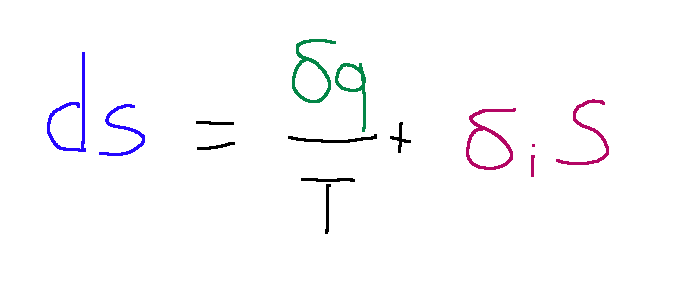
We can now give the following definitions for the following processes:
-the process is said to be adiabatic if

is equal to zero
(The entropy variation corresponds exactly to the internal entropy variation since the heat variation is equal to zero)
-the process is said to be isentropic if

is equal to zero
(the entropy change is zero)
-the process is said to be reversible if

is equal to zero
(The internal entropy change is zero)
-the process is said to be irreversible if

is greater than zero
(The change in internal entropy greater than zero)
Energy exchange in a wall-tent system
Let's start with the simplest system and then create its analogous situation in the field of electrical conductivity.
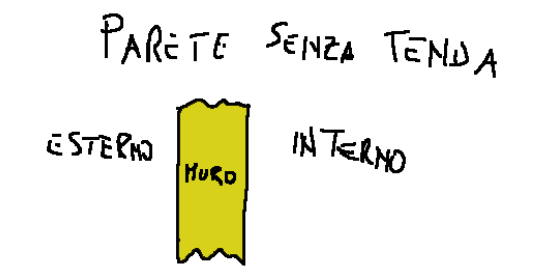
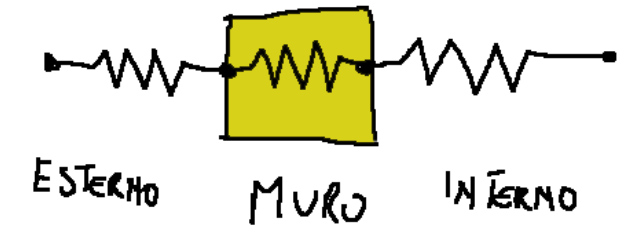
A simple system with one wall without a curtain is drawn below.
We can now obtain its similar conformation by researching in the field of electrical conductivity, here it is described below.
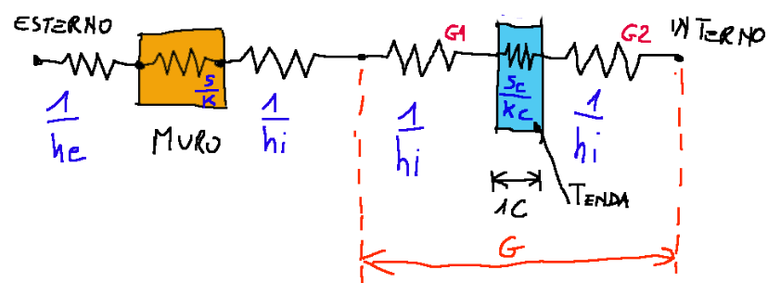
Now let's schematize the wall system with curtain

Its electrical analogue will appear as in the diagram below.
Considerations
If we were to add a curtain to the system proposed at the beginning we note that even if it had a thin layer, therefore S c which tends to 0, the insulation would still increase. In fact we note that in any case the group of resistances G will be formed in which G1 and G2 are also present.
Conclusions
G1 and G2 represent the convective motions that form near the tent, these thin layers of air function as insulators.
Request
Did you know that a curtain, even if thin, works as an object of insulation?

07-02-2024 - Fisica - Scambio di energia in un sistema muro-tenda [EN]-[IT]
Scambio di energia in un sistema muro-tenda
Concetti base
Le trasformazioni termodinamiche
Per comprendere le trasformazioni termodinamiche possiamo partire dal postulato che, in un sistema a massa costante, il flusso di entropia è legato solo al flusso di calore.
possiamo tradurre questo con la seguente formua
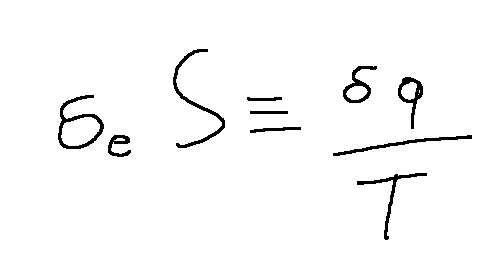
Da cui possiamo ricavare il bilancio dell'entropia:
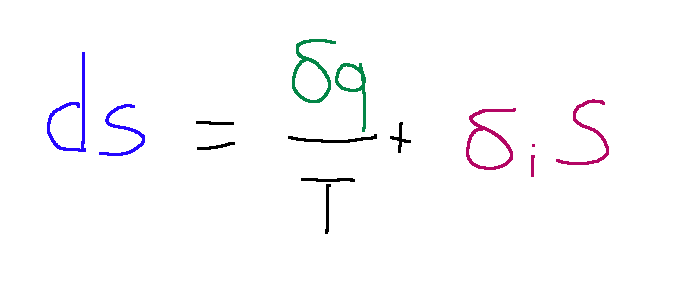
Possiamo ora dare le seguenti definizioni per i seguenti processi:
-il processo si dice adiabatico se

è uguale a zero
(La variazione di entropia corrisponde esattamente alla variazione di entropia interna essendo la variazione di calore è pari a zero)
-il processo si dice isoentropico se

è uguale a zero
(la variazione di entropia è zero)
-il processo si dice reversibile se

è uguale a zero
(La variazione di entropia interna è zero)
-il processo si dice irreversibile se

è maggiore di zero
(La variazione di entropia interna maggiore di zero)
Scambio di energia in un sistema muro-tenda
Partiamo con il sistema più semplice per poi creare la sua situazione analoga nel campo della conduttività elettrica.
Qui di seguito è disegnato un sistema semplice con una parete senza tenda.

Possiamo ora ricavare la sua conformazione analoga ricercando nel campo della conduttività elettrica, eccola qui sotto descritta.

Ora schematizziamo il sistema muro con tenda

Il suo analogo elettrico risulterà come nello schema qui sotto riportato.

Considerazioni
Se andassimo appunto ad aggiungere una tenda al sistema proposto all’inizio notiamo che se anche avesse uno strato sottile, quindi S c che tende a 0, la coibentazione aumenterebbe comunque. Infatti notiamo che comunque si formerà il gruppo di resistenze G in cui sono presenti anche G1 e G2.
Conclusioni
G1 e G2 rappresentano i moti convettivi che si vengono a formare nelle vicinanze della tenda, questi sottili strati d’aria funzionano come degli isolanti.
Domanda
Sapevate che una tenda, se pur sottile, funziona come oggetto di coibentazione?
THE END