
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

06-05-2025 - Physics - The magnetic field [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_32-31)
The magnetic field

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Description of the magnetic field
In ancient times, magnetite and its ability to attract iron filings were studied in particular. Perhaps these studies can be defined as the first studies on the magnetic field.
But what is a magnetic field?
A magnetic field is a region of space in which magnetic forces occur. It is generated by the movement of electric charges. For example, it can be generated by the flow of electrons present inside an electric wire or by atoms present in magnetic materials.
The intensity of the magnetic field is measured in Tesla (T).
Here is the formula for the magnetic field:
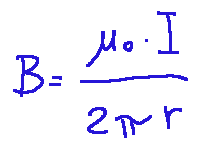
Where:
B = intensity of the magnetic field
𝜇 = magnetic permeability constant
I = electric current
r = distance from the wire
The Lorentz force
One of the fundamental concepts of electromagnetism is the Lorentz force. This is the force that acts on a charged particle in the presence of an electric field or in the presence of a magnetic field. Let's keep in mind that this force can act on a particle even in the presence of both fields, that is, both the electric and the magnetic fields.
Here is the formula for the Lorentz force.
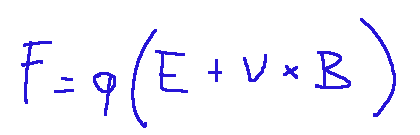
Where:
F = force experienced by the particle (Newton)
q = electric charge of the particle (Coulomb)
E = electric field (Volt/m)
v = velocity of the particle (m/s)
B = magnetic field (Tesla)
Note: v x B = vector product between velocity and magnetic field
This formula says that if the particle is still it is only subjected to the electric force where F = qe, while if the particle is moving, this formula shows that the magnetic field in turn generates a force that deflects the particle without changing its velocity.
In summary, we can say that Lorentz force describes the effect of electric and magnetic fields on charged particles.
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (1853-1928) was a Dutch theoretical physicist known for his fundamental contributions to electromagnetism and the theory of relativity.
Magnetic induction
There is a principle that underlies the functioning of electric generators, transformers and many technologies that we currently use. We are talking about magnetic induction. Magnetic induction is the phenomenon by which a magnetic field that varies over time generates an electric current in a conductor.
Magnetic induction is described by Faraday's law. This law states that a variation in magnetic flux through a circuit induces an electromotive force.
Below is the formula for magnetic induction or Faraday's law.
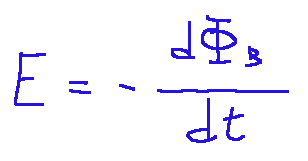
Where:
E = induced electromotive force (volts)
Φ B = magnetic flux (Tesla m²)
t = time
The minus sign (-) = indicates Lenz's principle, that is, that the induced current opposes the variation of the field
Circular and helical motions
These motions are often distorted and compared with those of mechanics. In reality, here we must think that we are within another topic, which is that of electrical engineering. In electrical engineering, circular motion occurs when a particle, such as an electric charge, moves along a circular path.
Still in electrical engineering, helical motion identifies a charge that enters a magnetic field with a speed oblique to the field lines.
The Earth's magnetic field
The Earth's magnetic field is the field generated by the planet Earth. This particular field is also called the geomagnetic field. The lines of the geomagnetic field have a similar arrangement in space to those of a common magnet and the lines exit from the magnetic north pole and enter the magnetic south pole.
The average intensity of the Earth's magnetic field is in a range between about 25 and 65 µT (microtesla).
The Van Allen Belts
The Van Allen belts are doughnut-shaped regions surrounding the Earth where high-energy charged particles (electrons and protons), mainly from the solar wind, are trapped. Then these particles are captured by the Earth's magnetic field and then captured. They will be forced to follow trajectories along the lines of force of the magnetic field. The Van Allen belts are studied in space engineering and in the design of electronic systems for high radiation environments.
Conclusions
The magnetic field is one of the fundamental forces of nature, essential for physics and modern technology. The magnetic field arises from the movement of electric charges. Electric motors, MRI, Defibrillators, Maglev, Compasses are all things that work through the magnetic field.
Question
Did you know that the Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in protecting the Earth from solar winds and charged particles from space?
Did you know that many species, such as birds and fish, use magnetism to orient themselves during migration?

ITALIAN

06-05-2025 - Fisica - Il campo magnetico [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_32-31)
Il campo magnetico

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Descrizione del campo magnetico
Nell'antichità si studiava in particolare la magnetite e la sua capacità di attirare
limatura di ferro. Forse questi studi possiamo definirli come i primi studi sul campo magnetico.
Ma che cosa è un campo magnetico?
Un campo magnetico è una regione dello spazio in cui si manifestano delle forze magnetiche. Esso è generato dal movimento di cariche elettriche. Ad esempio può essere generato dal flusso di elettroni presente all’interno di un filo elettrico o da atomi presenti nei materiali magnetici.
L'intensità del campo magnetico è misurata in Tesla (T).
Qui di seguito la formula del campo magnetico:
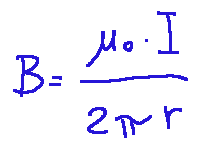
Dove:
B = intensità del campo magnetico
𝜇 = costante di permeabilità magnetica
I = corrente elettrica
r = distanza dal filo
La forza di Lorentz
Uno dei concetti fondamentale dell’elettromagnetismo è proprio la forza di Lorentz. Questa è la forza che agisce su una particella carica in presenza di un campo elettrico o in presenza di un campo magnetico. Teniamo presente che questa forza può agire su una particella anche in presenza di entrambi i campi, cioè sia di quello elettrico sia di quello magnetico.
Qui di seguito la formula della forza di Lorentz.
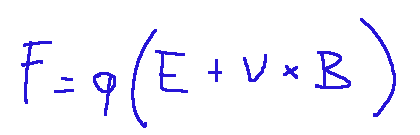
Dove:
F = forza subita dalla particella (Newton)
q = carica elettrica della particella (Coulomb)
E = campo elettrico (Volt/m)
v = velocità della particella (m/s)
B = campo magnetico (Tesla)
Nota: v x B = prodotto vettoriale tra velocità e campo magnetico
Questa formula dice che se la particella è ferma subisce solo la forza elettrica dove F = qe, mentre se la particella si muove, questa formula mostra che il campo magnetico genera a sua volta una forza che devia la particella senza modificarne la velocità.
In sintesi possiamo dire che forza di Lorentz descrive l'effetto di campi elettrici e magnetici sulle particelle cariche.
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (1853-1928) è stato un fisico teorico olandese conosciuto per i suoi contributi fondamentali all’elettromagnetismo e alla teoria della relatività.
L’induzione magnetica
C’è un principio che ha alla base del funzionamento dei generatori elettrici, dei trasformatori e di tantissime tecnologie che attualmente usiamo. Stiamo parlando proprio dell’induzione magnetica. L’induzione magnetica è quel fenomeno per cui un campo magnetico variabile nel tempo genera una corrente elettrica in un conduttore.
L’induzione magnetica è descritta dalla legge di Faraday. Questa legge afferma appunto che una variazione di flusso magnetico attraverso un circuito induce una forza elettromotrice.
Qui di seguito la formula dell’induzione magnetica o della legge di Faraday.
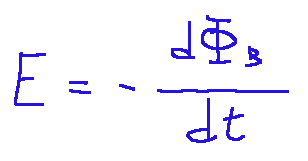
Dove:
E = forza elettromotrice indotta (volt)
Φ B = flusso magnetico (Tesla·m²)
t = il tempo
Il segno meno (-) = indica il principio di Lenz, cioè che la corrente indotta si oppone alla variazione del campo
I moti circolare ed elicoidale
Spesso questi moti vengono travisati e comparati con quelli della meccanica. In realtà qui dobbiamo pensare che siamo all’interno di un altro argomento, che è quello dell’elettrotecnica. In elettrotecnica il moto circolare avviene quando una particella, ad esempio una carica elettrica, si muove lungo una traiettoria circolare.
Sempre in ambito elettrotecnico, il moto elicoidale, identifica una carica che entra in un campo magnetico con una velocità obliqua rispetto alle linee del campo.
Il campo magnetico terrestre
Il campo magnetico terrestre è il campo generato dal pianeta Terra. Questo particolare campo è anche detto campo geomagnetico. Le linee del campo geomagnetico hanno una disposizione nello spazio simile a quelle di una comune calamita e le linee escono dal polo nord magnetico ed entrano nel polo sud magnetico.
L’intensità media del campo magnetico terrestre si colloca in un intervallo compreso tra circa 25 e 65 µT (microtesla).
Le fasce di Van Allen
Le fasce di Van Allen sono zone a forma di ciambella che circondano la Terra dove sono intrappolate particelle cariche ad alta energia (elettroni e protoni), provenienti principalmente dal vento solare. Quindi queste particelle vengono catturate dal campo magnetico terrestre e poi vengono catturate. Saranno così costrette a seguire traiettorie lungo le linee di forza del campo magnetico. Le fasce di Van Allen sono studiate nella ingegneria spaziale e nella progettazione di sistemi elettronici per ambienti ad alta radiazione.
Conclusioni
Il campo magnetico è una delle forze fondamentali della natura, essenziale per la fisica e la tecnologia moderna. Il campo magnetico nasce dal movimento delle cariche elettriche. Motori elettrici, Risonanza magnetica, Defibrillatori, Maglev, Bussole sono tutte cose che funzionano tramite il campo magnetico.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che il campo magnetico terrestre svolge un ruolo cruciale nel proteggere la Terra dai venti solari e dalle particelle cariche provenienti dallo spazio?
Lo sapevate che molte specie, come uccelli e pesci, usano il magnetismo per orientarsi durante le migrazioni?
THE END



