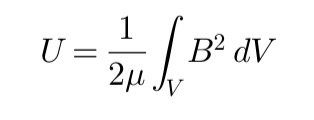
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

13-05-2025 - Physics - The energy of the magnetic field [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_21)
The energy of the magnetic field
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
The energy stored in an inductor
The formula for the energy stored in an inductor is next
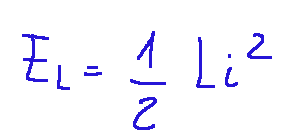
Where:
EL = energy stored in the inductor (in joules)
L = inductance (in henry)
i = current flowing in the inductor (in amperes)
We can consider this formula analogous to that of kinetic energy, to demonstrate this I report it here below:
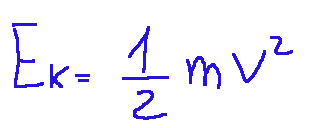
Where:
Ek = kinetic energy (in joules)
m = mass of the body (in kilograms)
v = velocity of the body (in meters per second)
So, what is the energy stored in an inductor?
The energy stored in an inductor is the energy that is accumulated in the magnetic field generated by the electric current flowing through the inductor.
In transformers, electronic filters and power circuits this is a fundamental property. Basically the inductor stores energy when the current increases and releases it when the current decreases. This work that we have just described contributes to the stability of the electric circuit.
Magnetic energy density
Magnetic energy density represents the energy stored in a magnetic circuit per unit volume. It is a fundamental quantity of electromagnetism.
Mathematically it is expressed as follows:
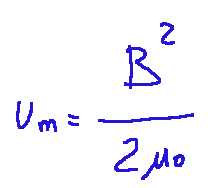
Where:
um = magnetic energy density
B = magnetic field intensity (in tesla, T)
𝜇0 = magnetic permeability of vacuum
The concept of magnetic density has been studied by several scientists: James Clerk Maxwell, Michael Faraday, Oliver Heaviside.
Maxwell used his equations of electromagnetism to show that fields carry energy and then studied the total energy density in the magnetic field.
Maxwell revolutionized the whole concept of magnetism in his time, as he was able to demonstrate that even a vacuum, filled with a magnetic field, can be a reservoir of energy with a defined density.
Magnetic energy in coupled circuits
Here we begin to enter a more complicated area and we have to bring out the concept of mutual induction. Magnetic energy in coupled circuits is the energy stored in the magnetic field generated by two inductors that interact with each other through the phenomenon of mutual induction. This is exactly what happens technically. But let's try to explain in simple words what this means. We can say that when two circuits are magnetically coupled, a change in current in one of them will induce a voltage in the other. Thus, a transfer of energy occurs between the two systems.
The total energy stored in a system of two mathematically coupled inductors is expressed as follows:
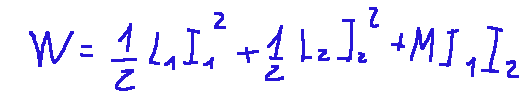
Where:
L1, L2 = inductances of the two circuits
I1, I2 = currents in the two inductors
M = mutual induction coefficient
Why is this concept important?
The study of magnetic energy in coupled circuits is fundamental in power circuits. In these circuits, the transfer of magnetic energy between windings allows voltages and currents to be regulated efficiently.
NOTE: In asynchronous motors the concept of magnetic energy in coupled circuits is fundamental for their operation and we know well how the world today moves mainly through asynchronous motors.
The concept of magnetic energy in coupled circuits is quite important even if I am sure that many of us have not heard of it. Let's think about asynchronous motors, which work precisely on the basis of this concept, they have a stator and a rotor. The rotating magnetic field generated by the stator induces a current in the rotor, thus creating a driving torque.
Let's remember that it was Nikola Tesla who patented the three-phase system of asynchronous motors in 1888 by studying the rotating magnetic field and magnetic energy in coupled circuits.
Conclusions
Magnetic energy density is an important concept that is taken into account when designing electric motors and transformers. Energy does not reside in wires or magnets, but in the magnetic field itself, spread in space, so even a vacuum can contain energy, if there is a magnetic field. The first to intuit this was the Scottish physicist Maxwell.
Question
The American scientist Henry was the first to publish scientific data on how a coil can create a magnetic field that, by varying, generates a voltage in itself, but did you know that in reality the Englishman Faraday did it first, but I do not publish the data of those experiments?
Another thing ... we talked about the concept of magnetic energy density.
Did you know that the concept of magnetic energy density is essential to guarantee the safety of machines that perform magnetic resonance imaging?

ITALIAN

13-05-2025 - Fisica - L’energia del campo magnetico [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_21)
L’energia del campo magnetico

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
L'energia immagazzinata in un'induttanza
La formula dell'energia immagazzinata in un’induttanza è la seguente
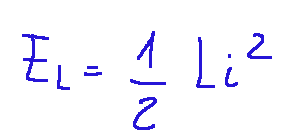
Dove:
EL = energia immagazzinata nell'induttore (in joule)
L = induttanza (in henry)
i = corrente che scorre nell'induttore (in ampere)
Possiamo ritenere questa formula analoga a quella dell’energia cinetica, per dimostrarlo la riporto qui sotto:
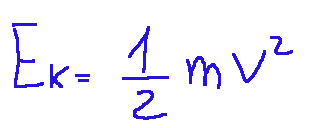
Dove:
Ek = energia cinetica (in joule)
m = massa del corpo (in chilogrammi)
v = velocità del corpo (in metri al secondo)
Quindi, che cos’è l’energia immagazzinata in un’induttanza?
L’energia immagazzinata in un’induttanza è l’energia che viene accumulata nel campo magnetico generato dalla corrente elettrica che attraversa l’induttore.
Nei trasformatori, nei filtri elettronici e nei circuiti di alimentazione questa è una proprietà fondamentale. Sostanzialmente l’induttore immagazzina energia quando la corrente aumenta e la rilascia quando la corrente diminuisce. Questo lavoro che abbiamo appena descritto contribuisce alla stabilità del circuito elettrico.
La densità di energia magnetica
La densità di energia magnetica rappresenta l’energia immagazzinata in un circuito magnetico per unità di volume. Essa è una grandezza fondamentale dell’elettromagnetismo.
Matematicamente si esprime come segue:
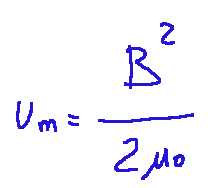
Dove:
um = densità di energia magnetica
B = intensità del campo magnetico (in tesla, T)
𝜇0 = permeabilità magnetica del vuoto
Il concetto di densità magnetica è stato studiato da diversi scienziati: James Clerk Maxwell, Michael Faraday, Oliver Heaviside.
Maxwell usò le sue equazioni dell’elettromagnetismo per dimostrare che i campi trasportano energia e poi studiò la densità di energia totale nel campo magnetico.
Maxwell a suo tempo rivoluzionò tutto il concetto del magnetismo, in quanto riuscì a dimostrare che anche il vuoto, intriso di un campo magnetico, può essere un serbatoio di energia con una densità definita.
L’energia magnetica in circuiti accoppiati
Qui iniziamo ad entrare in una zona più complicata e dobbiamo tirar fuori il concetto di mutua induzione. L’energia magnetica nei circuiti accoppiati è l’energia immagazzinata nel campo magnetico generato da due induttori che interagiscono tra loro attraverso il fenomeno della mutua induzione. Questo è esattamente quello che avviene tecnicamente. Proviamo però a spiegare con parole semplici che cosa significa questo. Possiamo dire che quando due circuiti sono magneticamente accoppiati, una variazione di corrente in uno di essi indurrà una tensione nell’altro. Così avviene un trasferimento di energia tra i due sistemi.
L'energia totale immagazzinata in un sistema di due induttori accoppiati matematicamente si esprime così:
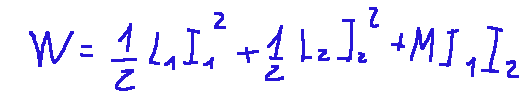
Dove:
L1, L2 = induttanze dei due circuiti
I1, I2 = correnti nei due induttori
M = coefficiente di mutua induzione
Perché è importante questo concetto?
Lo studio dell’energia magnetica nei circuiti accoppiati è fondamentale nei circuiti di potenza. In questi circuiti il trasferimento di energia magnetica tra avvolgimenti permette di regolare tensioni e correnti in modo efficiente.
NOTA: Nei motori asincroni il concetto di energia magnetica nei circuiti accoppiati è fondamentale per il loro funzionamento e sappiamo bene come il mondo oggi si muova soprattutto attraverso motori asincroni.
Il concetto di energia magnetica nei circuiti accoppiati è piuttosto importante anche se sono sicuro che molti di noi non ne hanno sentito parlare. Pensiamo proprio ai motori asincroni, che funzionano proprio in base a questo concetto, essi hanno uno statore ed un rotore. Il campo magnetico rotante generato dallo statore induce una corrente nel rotore, creando così una coppia motrice.
Ricordiamo che fu Nikola Tesla a brevettare il sistema trifase dei motori asincroni nel 1888 studiando proprio il campo magnetico rotante e l’energia magnetica in circuiti accoppiati.
Conclusioni
La densità di energia magnetica è un concetto importante che si tiene conto durante la progettazione di motori elettrici e trasformatori. L’energia non risiede nei fili o nei magneti, ma nel campo magnetico stesso, diffuso nello spazio, quindi anche il vuoto può contenere energia, se vi è un campo magnetico. Il primo ad intuire questo fu il fisico scozzese Maxwell.
Domanda
Lo scienziato americano Henry fu il primo a pubblicare dati scientifici su come una bobina può creare un campo magnetico che, variando, genera una tensione in se stessa, ma lo sapevate che in realtà lo fece prima l’inglese Faraday, ma non pubblico i dati di quegli esperimenti?
Altra cosa… abbiamo parlato del concetto di densità di energia magnetica.
Lo sapevate che il concetto di densità di energia magnetica è fondamentale per garantire la sicurezza dei macchinari che eseguono la risonanza magnetica?
THE END