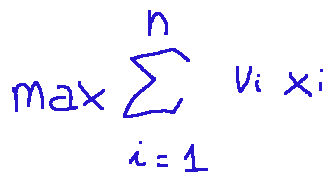~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

11-08-2025 - Operations Research - Binary Knapsack [EN]-[IT]
With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic in question.
(code notes: X_75)
Binary Knapsack
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
Operations research is a branch of applied mathematics that analyzes and solves problems to determine the best decision to make when faced with a complex problem.
Binary Knapsack
The binary knapsack is a classic version of the knapsack problem with the following characteristics.
We have n objects, each with a value vi and a weight wi, but the knapsack has a maximum capacity to take into account; this capacity will be W. Then we consider a binary decision variable xi for each object; that is, this variable will take the value 0 or 1.
xi will be handled as follows:
xi=1 if I take the object
xi=0 if I don't take the object
The mathematical formula will be as follows:
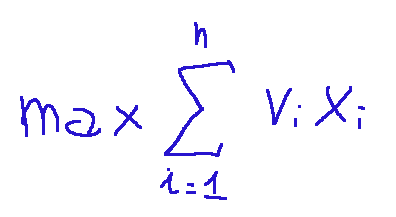
Where:
-MAX indicates that we want to maximize something
-This...
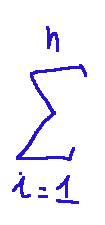
is a sum that starts from i=1 and ends at i=n (which in this case means considering all objects)
-vi is the value associated with object i
-xi is the binary decision variable
-vixi is the total value or contribution of object i, that is, if xi=1 the object contributes its value vi, if xi=0 its contribution will be zero.
In other words, we can say that the formula above means we want to sum the values of all the selected objects and find the combination that maximizes this sum.
Let's continue with the problem by writing it in mathematical form, and then I'll provide a description of the mathematical expression.
What we wrote above, given the given problem, will be subject to the following:
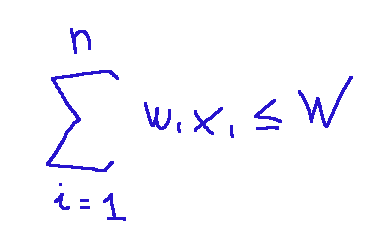
This expression tells us that the sum of the weights of the selected objects must not exceed the available capacity; that is, if W is equal to 15 kg, the weight of the objects inside the backpack must be less than or equal to 15 kg.
This expression is the heart of the mathematical model of the binary knapsack.
At this point we need to focus on our variables.
xi belongs to a set of values that are only positive integers and range only from 0 to 1.
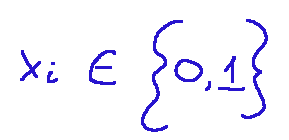
and we know that i ranges from 1 to n.

The Knapsack Interpretation
This This problem is certainly the most iconic in the field of Operations Research. The goal is to decide which objects to include to maximize total value, without exceeding capacity.
Solving this problem leads to the implementation of a method.
Once we learn this method, we can apply it to study many things. Here are some examples:
- Optimal vehicle loading (useful in logistics)
- Choosing the best investments when on a limited budget (useful in business)
- Selecting components for a product with cost constraints (useful for grocery shopping)
Who invented the Binary Knapsack Problem?
There is no official inventor. The Knapsack problem emerged in operations research studies during the 20th century. However, we know that George Dantzig and Ralph Gomory formalized precise mathematical versions of the knapsack, especially in integer linear programming.
George Dantzig was an American mathematician with a PhD in mathematics, who also invented the simplex method.
Ralph Gomory was also an American mathematician who earned his PhD in 1954 and made numerous contributions to integer linear programming.
Conclusions
The binary knapsack is a combinatorial optimization problem that reveals the most useful subset of objects to maximize a value. Its main characteristic is that the decision variables are binary. You may never have heard of this technique, but it is widely used in many applications: in logistics, resource planning, finance, manufacturing, and other sectors.
Question
Did you know that Dantzig and Gomory, both American mathematicians with PhDs in mathematics, laid the foundation for operations research, which is still taught in universities today? Did you know that Gomory was director of Research and Development at IBM?

ITALIAN

11-08-2025 - Ricerca operativa - Knapsack binario [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_75)
Knapsack binario
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Ricerca operativa è una disciplina della matematica applicata che si occupa di analizzare e risolvere problemi con il fini di capire qual è la decisione migliore da prendere davanti ad un problema complesso.
Knapsack binario
Lo Knapsack binario è una versione classica del problema dello zaino che ha le seguenti caratteristiche.
Abbiamo n oggetti, ognuno con un valore vi e un peso wi, ma lo zaino ha una capacità massima da tenere in considerazione questa capacità sarà W. Poi consideriamo una variabile decisionale binaria xi per ogni oggetto, cioè, questa variabile assumerà il valore di 0 o 1.
xi verrà gestita così:
xi=1 se prendo l'oggetto
xi=0 se non prendo l'oggetto
La formula matematica sarà la seguente:
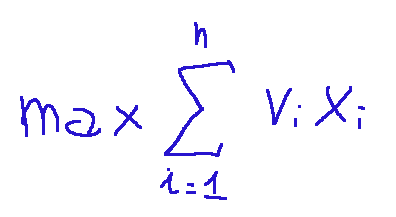
Dove:
-MAX indica che vogliamo massimizzare qualcosa
-Questo...

è una somma che parte da i=1 e arriva a i=n (che in questo caso significa considerare tutti gli oggetti)
-vi è il valore associato all'oggetto i
-xi è la variabile decisionale binaria
-vixi è il valore totale o il contributo dell'oggetto i, cioè se xi=1 l'oggetto contribuisce con il suo valore vi, se xi=0 il suo contributo sarà zero.
In altre parole possiamo dire che la formula scritta qui sopra significa che vogliamo effettuare la somma del valore di tutti gli oggetti scelti e trovare la combinazione che massimizza questa somma
Procediamo con il problema sempre scrivendolo in forma matematica e poi fornirò una descrizione della scrittura matematica
quello che abbiamo scritto prima, visto il problema dato sarà soggetto a quanto segue:
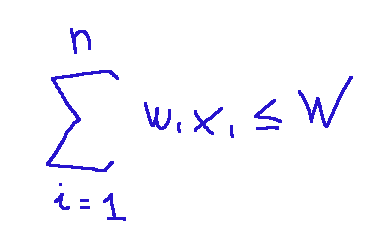
Questa scrittura ci indica che la somma dei pesi degli oggetti scelti non deve essere maggiore della capacità disponibile, cioè se W è uguale a 15kg, il peso degli oggetti all'interno dello zaino dovrà essere minore o uguale a 15kg.
Questa scritta è il cuore del modello matematico del knapsack binario.
a questo punto dobbiamo focalizzare le nostre variabili.
xi appartiene ad un insieme di valori che sono solo numeri interi positivi e sono solo da 0 a 1.
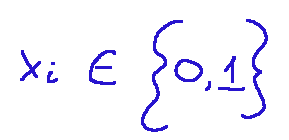
e sappiamo che i va da 1 a n

L'interpretazione del Knapsack
Questo problema, è sicuramente il più iconico della materia chiamata Ricerca Operativa. L'obiettivo è decidere quali oggetti mettere dentro per massimizzare il valore totale, senza superare la capacità.
La risoluzione di questo problema porta all'implementazione di un metodo.
Una volta imparato questo metodo possiamo applicarlo per studiare tante cose, qui di seguito alcuni esempi:
-Il carico ottima di un veicolo (utile nell'ambito della logistica)
-Scegliere gli investimenti più giusti da fare quando si ha un budget limitato (utile nell'ambito aziendale)
-Selezione di componenti per un prodotto con vincoli di costo (utile per fare la spesa)
Da chi nasce l'idea del problema del Knapsack binario
Non c'è un ideatore ufficiale. Lo Knapsack problem è emerso negli studi di ricerca operativa durante il XX secolo. Possiamo però che George Dantzig e Ralph Gomory hanno formalizzato versioni matematiche precise del knapsack, specialmente nella programmazione lineare intera.
George Dantzig è stato un matematico statunitense con PhD in matematica, inventore anche del metodo del simplesso.
Ralph Gomory era anche lui un matematico statunitense che ottenne la PhD nel 1954, diedi tantissimi contributi alla programmazione lineare intera.
Conclusioni
Il knapsack binario è un problema di ottimizzazione combinatoria che rivela qual è il sottoinsieme di oggetti più utile per massimizzare un valore. La sua caratteristica principale è che le variabili decisionali sono binarie. Forse non avrete mai sentito parlare di questa tecnica, ma è ampiamente usata in tante applicazioni: in logistica, pianificazione risorse, finanza, produzione e altri settori.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che Dantzig e Gomory, entrambi matematici statunitensi con dottorato in matematica, hanno creato le basi della ricerca operativa che tutt'oggi viene insegnata nelle università? Lo sapevate che Gomery fu direttore della Ricerca e Sviluppo in IBM?
THE END