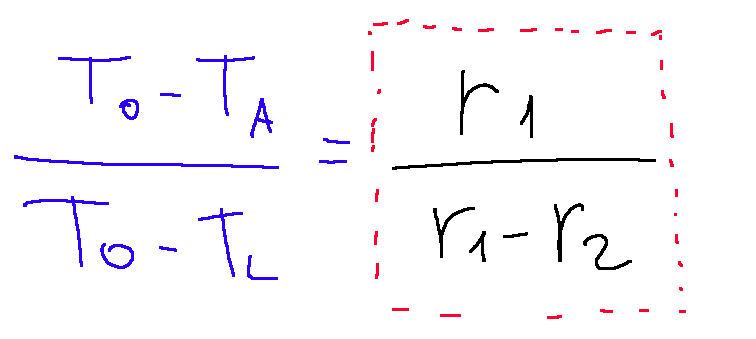
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
04-02-2024 - Physics - Conduction of a plate composed of two materials [EN]-[IT]
Conducting a plate composed of two materials
Basic concepts
From the second law of thermodynamics we know the following:
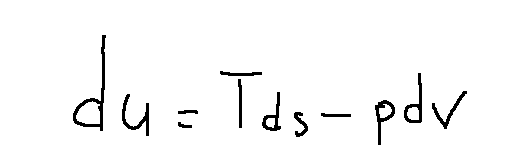
We can mathematically translate the second law of thermodynamics for an isolated system as follows:
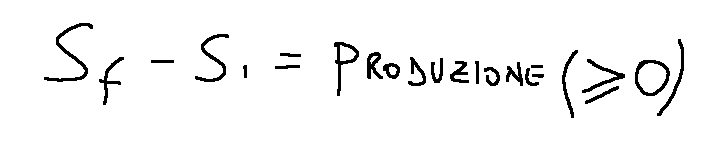
Where:
S = entropy
The second law of thermodynamics is based on the introduction, or intuition, of a state function called entropy (S).
This principle states that the entropy of an isolated system far from thermal equilibrium tends to increase until equilibrium is reached.
We also remember:
-In an isolated system the internal energy is constant, in fact ΔU=0.
-In an isolated system the quantities of heat pass from bodies at a higher thermodynamic temperature to bodies at a lower thermodynamic temperature.
-Absolute temperature is measured in degrees Kelvin (#K)
Conducting a plate
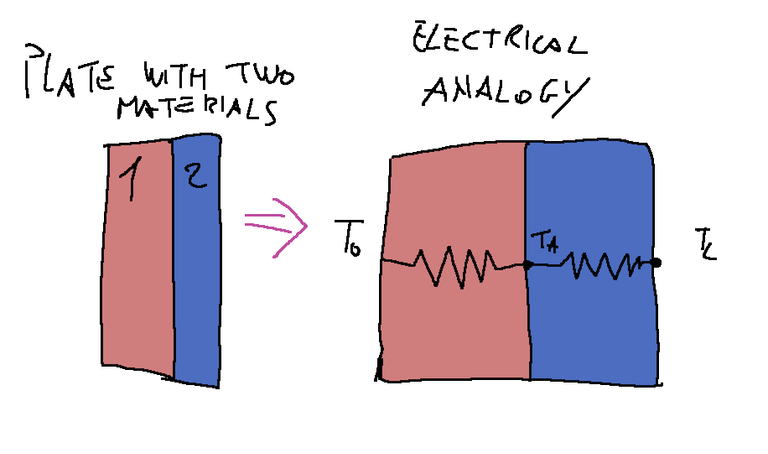
Let's consider a stationary plate, image shown below.
In physics a stationary state means fixed energy.
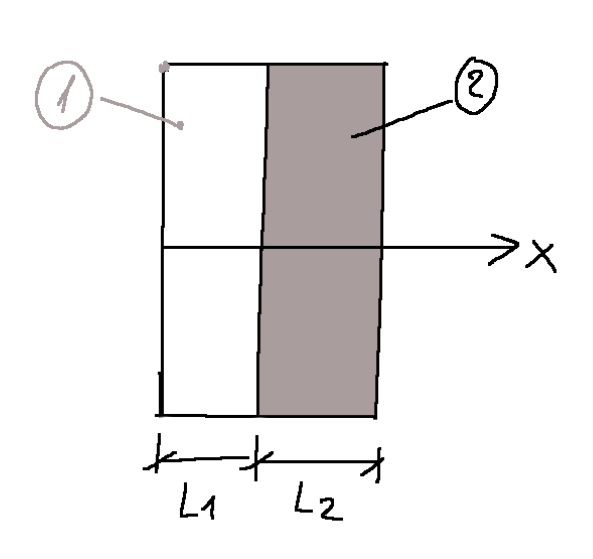
1-Layer of a certain type of material
2-Layer of a certain type of material different from the first
For a system like that of the plate shown in the figure, the following relations apply:
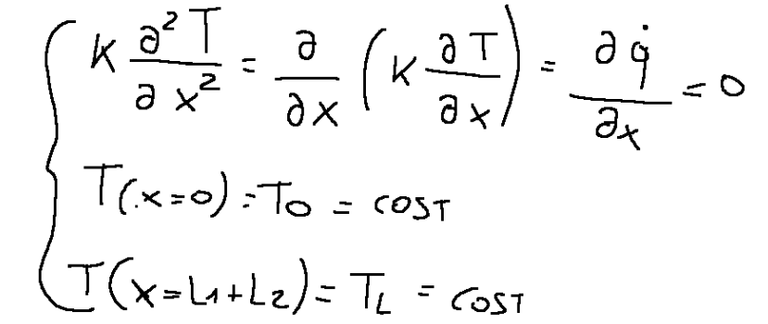
To try to know the temperature flow based on electrical analogy
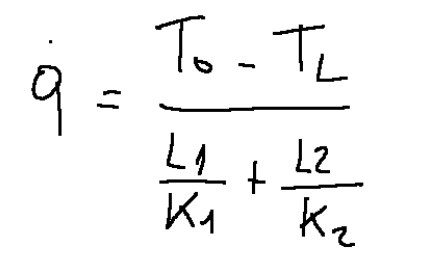
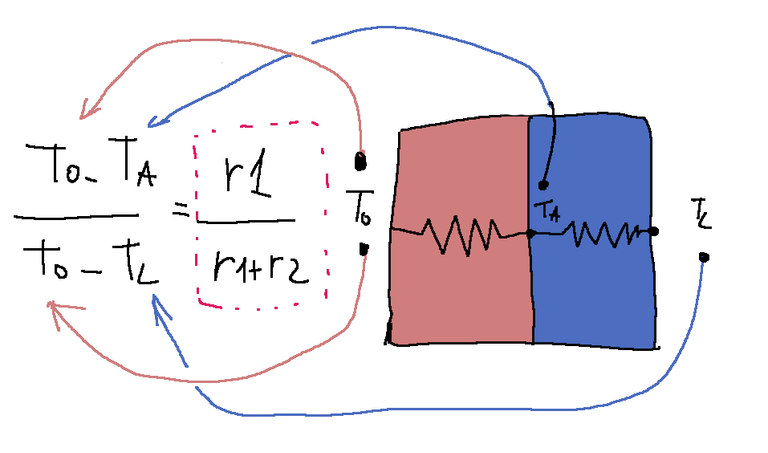
From this last formula we can derive a formula containing T A.
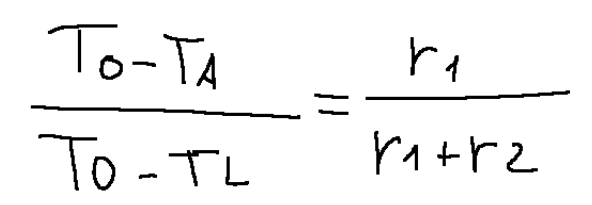
We can now come to some considerations.
Since T A is the only unknown we can say the following.
The percentage of temperature lost when passing through the thickness of material 1 is equal to the resistivity of material 1 compared to the resistivity of the entire sheet.
Conclusions
Considering the flow that passes through a plate composed of two materials we can say that the percentage of temperature lost in degrees when passing through the thickness of material 1 is equal to the resistivity of material 1 compared to the resistivity of the entire plate.
Request
In winter, when I was little, I always felt the cold coming into the house, so for me it was the cold going towards the heat. Has the concept always been clear to you that the quantity of heat passes from hot to cold?

04-02-2024 - Fisica - Conduzione di una lastra composta di due materiali [EN]-[IT]
Conduzione di una lastra composta di due materiali
Concetti base
Dalla seconda legge della termodinamica sappiamo quanto segue:
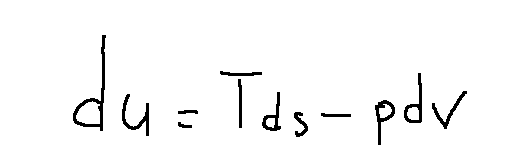
Possiamo tradurre matematicamente la seconda legge della termodinamica per un sistema isolato come segue:
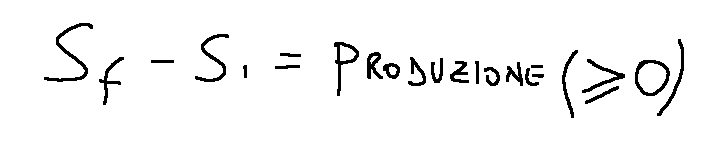
dove:
S = entropia
La seconda legge della termodinamica si basa sull'introduzione, o l'intuizione, di una funzione di stato chiamata entropia (S).
Questo principio afferma che l'entropia di un sistema isolato lontano dall'equilibrio termico tende ad aumentare fino a quando l'equilibrio non viene raggiunto.
Ricordiamo inoltre:
-In un sistema isolato l'energia interna è costante, infatti ΔU=0.
-In un sistema isolato le quantità di calore passano da corpi a temperatura termodinamica superiore a corpi a temperatura termodinamica inferiore.
-La temperatura assoluta si misura in gradi Kelvin (#K)
Conduzione di una lastra
Consideriamo una lastra stazionaria, immagine riportata qui sotto.
In fisica una stato stazionario significa ad energia fissata.

1-Strato di una certa tipologia di materiale
2-Strato di una certa tipologia di materiale diverso dal primo
Per un sistema come quello della lastra mostrata in figura valgono le seguente relazioni:
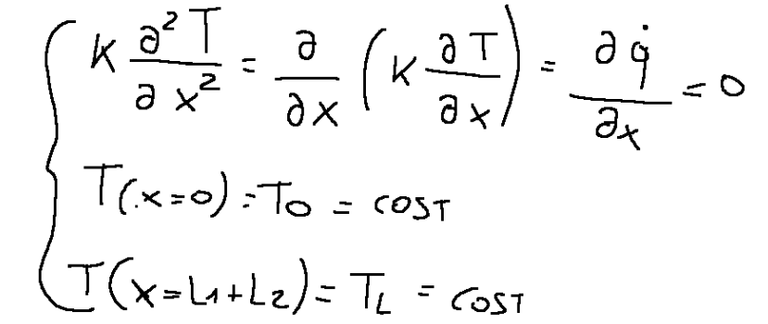
Per provare a conoscere il flusso di temperatura basandosi sull’analogia elettrica
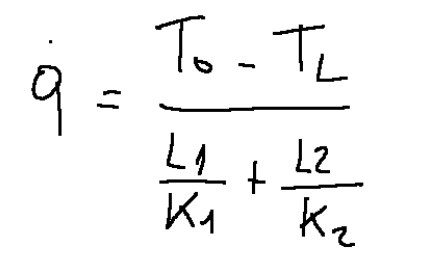
Da quest’ultima formula possiamo ricavare una formula in cui è contenuta T A.
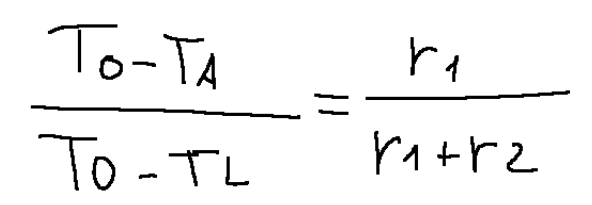
Possiamo ora arrivare ad alcune considerazioni.
Essendo T A l’unica incognita possiamo dire quanto segue.
La percentuale di temperatura persa quando si attraversa lo spessore del materiale 1 è pari alla resistività del materiale 1 rispetto alla resistività dell’intera lastra.
Conclusioni
Considerando il flusso che attraversa una lastra composta da due materiale possiamo dire che la percentuale di temperatura persa in gradi quando si attraversa lo spessore del materiale 1 è pari alla resistività del materiale 1 rispetto alla resistività dell’intera lastra.
Domanda
D'inverno, quando ero piccolo, sentivo sempre il freddo che entrava in casa, quindi per me era il freddo che andava verso il caldo. Vi è sempre stato chiaro il concetto che invece la quantità di calore passa dal caldo al freddo?
THE END