~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

15-05-2025 - Physics - James Clerk Maxwell [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_19)
James Clerk Maxwell
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
James Clerk Maxwell, who was he?
I couldn't help but dedicate an article entirely to him.
On June 13, 1831, in Edinburgh, Scotland, James Clerk Maxwell was born.
Perhaps he is not as well-known a name as he should be, in fact Maxwell is considered one of the greatest physicists in history, on a par with Newton and Einstein.
Einstein himself said “Maxwell’s equations are the deepest content that nature has ever revealed to us”
The four equations
Maxwell is famous for his 4 equations that completely describe how electric and magnetic fields behave and interact.
Below I report all 4 laws in sequence.
Maxwell’s First Law
This law is also known as Gauss’s Law for the electric field.
Mathematically it looks like this:
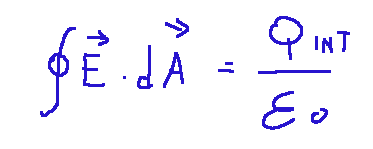
Where:
∮ = Closed surface integral symbol, indicates that the integration is performed on a closed surface.
E = Electric field vector, represents the intensity and direction of the electric field at a point on the surface
dA = Differential area vector, represents an infinitesimal element of the surface, oriented perpendicular to it.
Q int = Total charge enclosed within the closed surface
ε0 = Vacuum permittivity, a constant that characterizes the capacity of space to allow the propagation of electric field lines.
What does it say?
Maxwell's first law tells us that the electric field is generated by electric charges.
Maxwell's second law
This law is also known as Gauss's law for the magnetic field
Mathematically it looks like this:
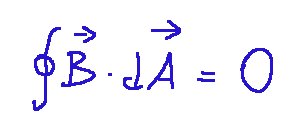
Where:
∮ = Closed surface integral symbol
B = Magnetic field vector, represents the intensity and direction of the magnetic field at each point on the surface.
dA = Differential area vector
0 = The result of the integral is always zero, since there are no magnetic monopoles.
What does it say?
Maxwell's second law states that there are no magnetic charges (magnetic monopoles); magnetic field lines are always closed.
Maxwell's third law
This law is also known as Faraday's Law
Mathematically it looks like this:
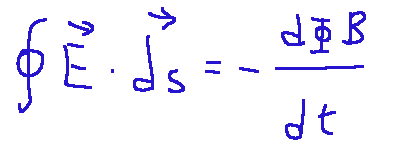
Where:
∮ = Line integral symbol, indicates that the integration occurs along a closed curve.
E = Electric field vector.
ds = Differential element of length of the curve
ΦB = Magnetic flux through a surface bounded by the closed curve.
dΦB/dt = Derivative of the magnetic flux with respect to time, indicates the variation of the magnetic field
The sign - = Represents the opposite direction of the induced electric field with respect to the variation of the magnetic field, according to Lenz's law.
What does it say?
A variable magnetic field generates an electric field
Maxwell's fourth law
This law is also known as the Ampère-Maxwell Law
Mathematically it looks like this:
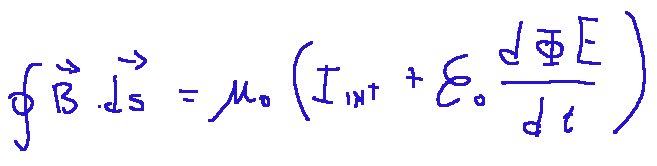
Where:
∮ = Line integral symbol, indicates that the integration occurs along a closed curve.
B = Magnetic field vector
ds = Differential length element of the curve.
μ0 = Permeability of vacuum
I int = Total electric current enclosed within the closed curve.
ΦE = Electric flux through a surface delimited by the closed curve
dΦB/dt = Derivative of the electric flux with respect to time, indicates the variation of the electric field.
What does he say?
An electric current or a variable electric field generates a magnetic field
What else did Maxwell intuit?
He saw light differently
One of his most brilliant intuitions was to understand already in his historical period that light is an electromagnetic wave.
The first color photograph
Maxwell intuited that by using the three color filters of red, green and blue, a color image could be obtained. Not many people know this, but the idea of the first color photograph is attributed to him.
He saw all the colors
He demonstrated that the colors perceptible by our brain and transmittable by our eye could be obtained by mixing red, green and blue light with different percentages, giving rise to the RGB principle, a principle still used today in digital.
Conclusions
James Clerk Maxwell laid the foundations of modern physics by unifying electricity, magnetism and light in a single theory. We can also think that Maxwell built the theoretical foundations of the technology of the contemporary world.
Question
The world today runs on alternating current and it was Tesla who designed the three-phase asynchronous motor that runs on alternating current (the most used electric motor in the world).
Did you know that the invention of Tesla's asynchronous motor depends directly on the physical phenomena described by Maxwell's 4 laws?

ITALIAN

15-05-2025 - Fisica - James Clerk Maxwell [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_19)
James Clerk Maxwell
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
James Clerk Maxwell, chi era?
Non potevo non dedicare un articolo completamente a lui.
Il 13 giugno 1831 a Edimburgo, in Scozia, nacque James Clerk Maxwell.
Forse è un nome non tanto noto come in realtà dovrebbe essere, infatti Maxwell è considerato uno dei più grandi fisici della storia, al pari di Newton ed Einstein.
Lo stesso Einstein disse “Le equazioni di Maxwell sono il contenuto più profondo che la natura ci abbia mai rivelato”
Le quattro equazioni
Maxwell è celebre per le sue 4 equazioni che descrivono in maniera completa come si comportano e interagiscono i campi elettrici e magnetici.
Qui di seguito riporto in sequenza tutte le 4 leggi.
Prima legge di Maxwell
Questa legge è conosciuta anche come Legge di Gauss per il campo elettrico.
Matematicamente si presenta in questa maniera:
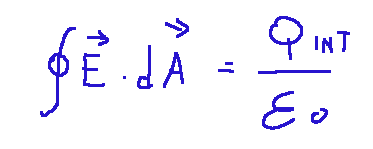
Dove:
∮ = Simbolo di integrale di superficie chiusa, indica che l'integrazione viene effettuata su una superficie chiusa.
E = Vettore del campo elettrico, rappresenta l'intensità e la direzione del campo elettrico in un punto della superficie
dA = Vettore di area differenziale, rappresenta un elemento infinitesimale della superficie, orientato perpendicolarmente ad essa.
Q int = Carica totale racchiusa all'interno della superficie chiusa
ε0 = Permittività del vuoto, una costante che caratterizza la capacità dello spazio di permettere la propagazione delle linee di campo elettrico.
Cosa afferma?
La prima legge di Maxwell ci dice che il campo elettrico è generato dalle cariche elettriche.
La seconda legge di Maxwell
Questa legge è conosciuta anche come Legge di Gauss per il campo magnetico
Matematicamente si presenta in questa maniera:
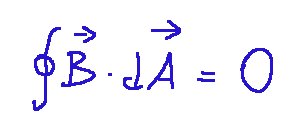
Dove:
∮ = Simbolo di integrale di superficie chiusa
B = Vettore del campo magnetico, rappresenta l'intensità e la direzione del campo magnetico in ogni punto della superficie.
dA = Vettore di area differenziale
0 = Il risultato dell'integrale è sempre zero, poiché non esistono monopoli magnetici.
Cosa afferma?
La seconda legge di Maxwell afferma che non esistono cariche magnetiche (monopoli magnetici); le linee del campo magnetico sono sempre chiuse.
La terza legge di Maxwell
Questa legge è conosciuta anche come Legge di Faraday
Matematicamente si presenta in questa maniera:
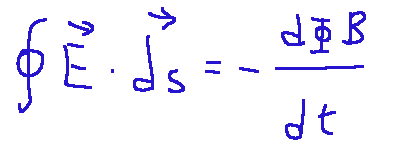
Dove:
∮ = Simbolo di integrale di linea, indica che l'integrazione avviene lungo una curva chiusa.
E = Vettore del campo elettrico.
ds = Elemento differenziale di lunghezza della curva
ΦB = Flusso magnetico attraverso una superficie delimitata dalla curva chiusa..
dΦB/dt = Derivata del flusso magnetico rispetto al tempo, indica la variazione del campo magnetico
Il segno - = Rappresenta la direzione opposta del campo elettrico indotto rispetto alla variazione del campo magnetico, secondo la legge di Lenz.
Cosa afferma?
Un campo magnetico variabile genera un campo elettrico
La quarta legge di Maxwell
Questa legge è conosciuta anche come Legge di Ampère-Maxwell
Matematicamente si presenta in questa maniera:
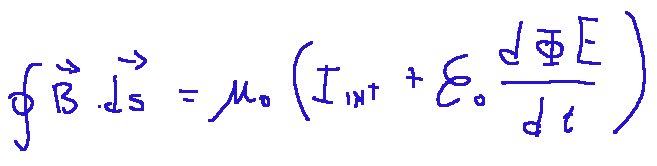
Dove:
∮ = Simbolo di integrale di linea, indica che l'integrazione avviene lungo una curva chiusa.
B = Vettore del campo magnetico
ds = Elemento differenziale di lunghezza della curva.
μ0 = Permeabilità del vuoto
I int = Corrente elettrica totale racchiusa all'interno della curva chiusa.
ΦE = Flusso elettrico attraverso una superficie delimitata dalla curva chiusa
dΦB/dt = Derivata del flusso elettrico rispetto al tempo, indica la variazione del campo elettrico.
Cosa afferma?
Una corrente elettrica o un campo elettrico variabile genera un campo magnetico
Cosa altro intuì Maxwell?
Vide la luce in maniera diversa
Una delle sue intuizioni più geniali fu quella di capire già nel suo periodo storico che la luce è un’onda elettromagnetica.
La prima fotografia a colori
Maxwell intuì che usando i tre filtri di colore rosso, verde e blu si poteva ottenere un’immagine a colori. Non molti lo sanno, ma l’idea della prima fotografia a colori è attribuita proprio a lui.
Egli vide tutti i colori
Egli dimostrò che i colori percepibili dal nostro cervello e trasmissibili dal nostro occhio potevano essere ottenuti mescolando con percentuali diverse luce rossa, verde e blu, dando origine al principio RGB, un principio ancora usato oggi nel digitale.
Conclusioni
James Clerk Maxwell pose le basi della fisica moderna unificando elettricità, magnetismo e luce in una sola teoria. Possiamo anche pensare che Maxwell ha costruito le fondamenta teoriche della tecnologia del mondo contemporaneo.
Domanda
Il mondo oggi va a corrente alternata e fu Tesla a progettare il motore asincrono trifase che funziona a corrente alternata (motore elettrico più usato al mondo).
Lo sapevate che l'invenzione del motore asincrono di Tesla dipende direttamente dai fenomeni fisici descritti dalle 4 leggi di Maxwell?
THE END
