
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

23-04-2025- Physics - Acoustic Waves [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_54-53-52)
Acoustic Waves

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction to acoustic waves
We can say that acoustic waves are mechanical waves that propagate through an elastic medium and are the basis of the phenomenon of sound.
Acoustic waves are formed when a source generates vibrations that are transmitted into the surrounding medium in the form of pressure variations.
Note: In physics, air, water or a solid are considered elastic mediums.
Let's try to think of a speaker that is designed to convert electrical signals into acoustic waves.
The main component of a speaker is a cone or a membrane that vibrates in response to an electrical signal. Basically, inside a speaker, the vibrations of the membrane cause pressure variations in the surrounding area, thus creating acoustic waves that will propagate in space. When these waves reach our ear, our brain will interpret them as sounds.
Acoustic waves in gases
Already from the title of this paragraph we understand that we are talking about acoustic waves that propagate in a gaseous medium. Acoustic waves in gases are a type of mechanical wave and propagate through pressure and density variations in the gaseous medium.
Important: this type of wave is longitudinal wave. This means that the direction of the gas particles' movement coincides with the direction of the wave's propagation.
As we wrote before, gas is defined as an elastic medium. The elastic property that characterizes the response to a pressure pulse on gas is the comprehensibility modulus, defined as the ratio between the pressure on a volume of gas and the relative variation of the gas volume.

Where:
B = compressibility modulus
P = applied pressure
V = volume
dV = infinitesimal change in volume
Elastic property of fluids and Young's modulus
With the help of experimentation, it has been observed that solid bodies are not ideal rigid bodies but rather, subjected to traction or compression stresses, they exhibit elastic behavior.
As regards the longitudinal elasticity of a medium or material, the so-called Young's modulus can help us. Young's modulus is also called the longitudinal modulus of elasticity, and is a physical quantity that measures the stiffness of a material when subjected to a tensile or compressive force along a direction.
Below is the formula for Young's modulus.
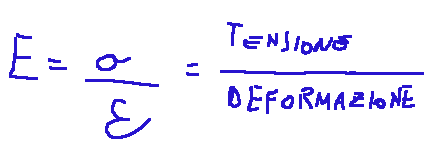
Where:
E = Young's modulus (in Pascal, Pa),
σ = tension (force per unit area),
ε = relative deformation (variation of length with respect to the initial length)
Energy characteristics of waves
First of all, let's clarify the concept that a mechanical wave is not characterized by the transport of matter. While it is true that through the propagation of the wave the ability to perform work is transmitted, that is, there is a propagation of mechanical energy.
So, here is a list of the energetic characteristics of waves:
Energy transported by the wave
Energy proportional to the amplitude
Intensity of the wave
Energy of electromagnetic waves
If we wanted to summarize everything regarding the energetic characteristics of waves, we can say that the wave propagates energy in the medium, that it has an amplitude characteristic, that it has an intensity that decreases with distance and has a frequency.
Sound Waves and Hearing
Sound waves are spherical longitudinal waves. This type of wave propagates through compression and rarefaction of the air, for this reason they are called longitudinal waves.
We also normally recognize that in an open environment, sound waves spread in all directions, thus forming a spherical shape.
Another characteristic of sound waves is the decrease in intensity with distance. Technically, the energy of the sound is distributed over an increasingly larger surface, as the wave moves away from the source. There is a relationship that links sound waves to distance, or rather there is a law that describes the relationship between intensity and distance. We know that in sound waves, by doubling the distance, the intensity of the sound becomes four times weaker.
The sound level is measured in decibels, symbol dB.
As far as our ear, that is, the one that perceives, we can say that we distinguish sounds based on three distinctive characteristics: intensity, pitch and timbre.
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is a physical phenomenon that describes the variation in the frequency of a wave perceived by an observer in motion with respect to the source of the wave itself. A classic example is how we perceive the sound of a siren as it approaches and comes towards us. We know that if the sound source approaches the observer, the perceived frequency increases.
We can summarize the concept as follows. The Doppler Effect describes the change in the perceived frequency of a wave when there is relative motion between the source and the observer
The general formula for sound is shown below:
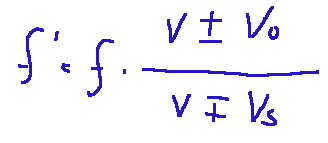
Where:
f ′ = frequency perceived by the observer
f = frequency emitted by the source
v = speed of sound in the medium
vo = speed of the observer
vs = speed of the source
Huygens-Fresnel Principle
This principle states that any point on the wavefront, for any wave and of any shape, can be considered a point source.
It is essentially a fundamental concept in wave optics and describes the propagation of light waves. This principle also states that every point of a light wave front can be seen as a secondary source of spherical waves.
This principle is not as well known as many others, but it is applied in the studies of diffraction, interference, and above all in modern optics. In fact, it is fundamental for designing lenses and optical fibers.
Conclusions
The physics of acoustic waves, the study of acoustic waves, allows us to better understand the sound world around us. Furthermore, in the last 50 years, studies on acoustic waves have expanded considerably also in the context of their diffusion at sea for underwater communications, sonar and surveys.
Question
Christian Doppler was an Austrian mathematician and physicist known in physics for having described the physical phenomenon today called the Doppler effect. During his life he published about 50 articles on mathematics, physics and astronomy. Yet, despite all this, did you know that at the beginning of his career he struggled to find stable employment as a teacher?

ITALIAN

23-04-2025 - Fisica - Onde acustiche [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_54-53-52)
Onde acustiche

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione alle onde acustiche
Possiamo dire che le onde acustiche sono onde meccaniche che si propagano attraverso un mezzo elastico e sono la base del fenomeno del suono.
Le onde acustiche si formano quando una sorgente genera vibrazioni che si trasmettono nel mezzo circostante sotto forma di variazione di pressione.
Nota: In fisica è considerato un mezzo elastico l’aria, l’acqua o un solido.
Proviamo a pensare ad una cassa acustica che è progettata per convertire segnali elettrici in onde acustiche.
Il componente principale di una cassa acustica è costituito da un cono o una membrana che vibra in risposta ad un segnale elettrico. Sostanzialmente all’interno di una cassa acustica le vibrazioni della membrana causano variazioni di pressione nell’area circostante, creando così delle onde acustiche che si propagheranno nello spazio. Quando queste onde arriveranno al nostro orecchio il nostro cervello le interpreterà come suoni.
Le onde acustiche nei gas
Già dal titolo di questo paragrafo capiamo che parliamo di onde acustiche che si propagano nel mezzo gassoso. Le onde acustiche nei gas sono un tipo di onda meccanica e si propagano attraverso variazioni di pressione e densità nel mezzo gassoso.
Importante: questa tipologia di onde, sono onde longitudinali. Questo vuol dire che la direzione del movimento delle particelle del gas coincide con la direzione di propagazione dell’onda stessa.
Come abbiamo scritto prima, il gas viene definito un mezzo elastico. La proprietà elastica che caratterizza la risposta ad un impulso di pressione su gas è il modulo di comprensibilità, definito come rapporto tra la pressione su un volume di gas e la variazione relativa del volume di gas.

Dove:
B = modulo di compressibilità
P = pressione applicata
V = volume
dV = variazione infinitesima di volume
Proprietà elastica dei fluidi e modulo di Young
Con l’aiuto della sperimentazione si è osservato che i corpi solidi non sono dei corpi rigidi ideali ma bensì sottoposti a sforzi di trazione o compressione, essi manifestano un comportamento elastico.
Per quanto riguarda l’elasticità longitudinale di un mezzo o di un materiale, ci può venire in aiuto il cosiddetto modulo di Young. Il modulo di Young viene chiamato anche modulo di elasticità longitudinale, ed è una grandezza fisica che misura la rigidità di un materiale quando viene sottoposto a una forza di trazione o compressione lungo una direzione.
Qui di seguito la formula del modulo di Young.
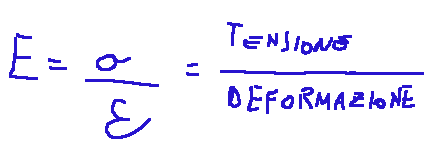
Dove:
E = modulo di Young (in Pascal, Pa),
σ = tensione (forza per unità di area),
ε = deformazione relativa (variazione di lunghezza rispetto alla lunghezza iniziale)
Caratteristiche energetiche delle onde
Innanzitutto, chiariamo il concetto che un onda meccanica non è caratterizzata dal trasporto di materia. Mentre invece è vero che attraverso la propagazione dell’onda si trasmette la capacità di compiere il lavoro, ovvero c’è una propagazione di energia meccanica.
Quindi, seguito un elenco delle caratteristiche energetiche delle onde:
Energia trasportata dall’onda
Energia proporzionale all’ampiezza
Intensità dell’onda
Energia delle onde elettromagnetiche
Se volessimo riassumere il tutto per quanto riguarda le caratteristiche energetiche delle onde, possiamo dire che l’onda propaga energia nel mezzo, che ha una caratteristica d’ampiezza, che ha un’intensità che diminuisce con la distanza ed ha una frequenza.
Onde sonore e udito
Le onde sonore sono onde longitudinali sferiche. Questa tipologia di onde si propaga tramite compressione e rarefazione dell’aria, per questo motivo vengono definite onde longitudinali.
Riconosciamo anche normalmente che in un ambiente aperto le onde sonore si diffondono in tutte le direzioni, formando così una forma sferica.
Un’altra caratteristica delle onde sonore è la diminuzione dell’intensità con la distanza. Tecnicamente l’energia del suono si distribuisce su una superficie sempre più ampia, man mano che l’onda si allontana dalla sorgente. C’è una relazione che lega le onde sonore alla distanza, anzi c’è una legge che descrive il rapporto che c’è tra l’intensità e la distanza. Sappiamo che nelle onde sonore raddoppiando la distanza, l’intensità del suono diventa quattro volte più debole.
Il livello sonoro si misura in decibel, simbolo dB.
Per quanto riguarda il nostro orecchio, ovvero quello che percepisce, possiamo dire che noi distinguiamo i suoni in base a tre caratteri distintivi: l’intensità, l’altezza ed il timbro.
Effetto Doppler
L’effetto Doppler è un fenomeno fisico che descrive la variazione della frequenza di un’onda percepita da un osservatore in movimento rispetto alla sorgente dell’onda stessa.un esempio classico è come percepiamo noi il suono di una sirena mentre si avvicina e viene verso di noi.sappiamo che se la sorgente sonora si avvicina all’osservatore, la frequenza percepita aumenta.
Possiamo sintetizzare il concetto come segue. L’Effetto Doppler descrive la variazione della frequenza percepita di un’onda quando c’è movimento relativo tra la sorgente e l’osservatore
Qui di seguito è mostrata la formula generale per il suono:
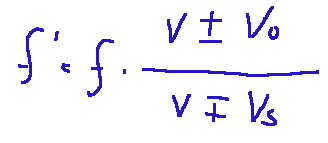
Dove:
f ′ = frequenza percepita dall'osservatore
f = frequenza emessa dalla sorgente
v = velocità del suono nel mezzo
vo = velocità dell’osservatore
vs = velocità della sorgente
Principio di Huygens-Fresnel
Questo principio afferma che ogni punto del fronte d’onda, per qualsiasi onda e di qualsiasi forma, può essere considerato una sorgente puntiforme.
Esso sostanzialmente è un concetto fondamentale nell’ottica ondulatoria e descrive la propagazione delle onde luminose. Questo principio afferma anche che ogni punto di un fronte d’onda luminoso può essere visto come una sorgente secondaria di onde sferiche.
Questo principio non è noto come tanti altri, ma viene applicato negli studi della diffrazione, nelle interferenze, e soprattutto nell’ottica moderna. Esso infatti è fondamentale per progettare lenti e fibre ottiche.
Conclusioni
La fisica delle onde acustiche, lo studio delle onde acustiche, ci permette di capire meglio il mondo sonoro attorno a noi. Inoltre negli ultimi 50 anni gli studi sulle onde acustiche si sono ampliate notevolmente anche nell'ambito della loro diffusione in mare per le comunicazioni subacquee, sonar e rilevamenti.
Domanda
Christian Doppler fu un matematico e fisico austriaco noto in fisica per aver descritto il fenomeno fisico chiamato oggi effetto Doppler. Durante la sua vita pubblicò circa 50 articoli su matematica, fisica e astronomia. Eppure, nonostante tutto ciò, lo sapevate che all'inizio della sua attività lavorativa fece fatica a trovare un impiego stabile come docente?
THE END