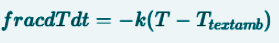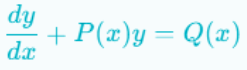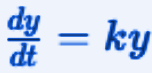
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

15-07-2025 - Mathematical Analysis - Differential Equations [EN]-[IT]
With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic mentioned above.
(code notes: X-47-46-45)
Differential Equations

Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
Differential equations are a special mathematical tool. We could say that they are used to tell us how things change over time. Differential equations are a way to describe changes. They are used to describe changes in the motion of bodies, in electromagnetism, thermodynamics, biology, economics, and even finance.
Differential equation, technical explanation
An ordinary differential equation of order n for y(t) is an equation in which an independent variable t, the (unknown) function y(t), and derivatives of the function y(t) appear, at most of order n.
Its general form is as follows:
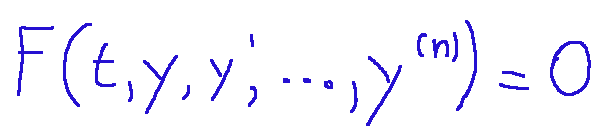
Any function y(t) differentiable n times on an open interval I that makes the equation identically satisfied (i.e., satisfied for every t in I) is called a solution or general integral of the equation.
NOTE: An ordinary differential equation can have exactly one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions at all.
First-order linear ordinary differential equation
Let's take the following equation as an example:
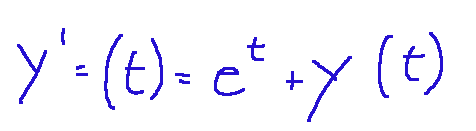
This is a first-order differential equation because the unknown function appears as a derivative only once. In this case, the independent variable is t, and the equation is also expressed in the following simplified form:
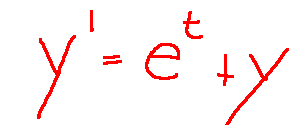
Considerations regarding the previous equation
The equation type is linear, first-order, and with constant coefficients.
Given an initial value, we can determine the constant (C) and obtain the unique solution that passes through that point.
The General Integral
Let's take the following differential equation as an example and find the general integral.
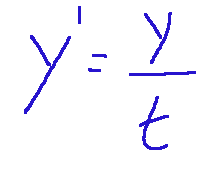
Without performing the various steps, I show below the general integral of the differential equation above:
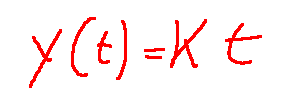
The general integral of a differential equation is the form with all constants that describes all the solutions. In fact, in the previous example, the term k represents the constant.
Systems of First-Order Differential Equations
Below is an example of a system of first-order differential equations in normal form:
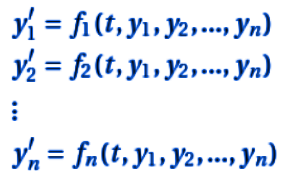
A system of first-order differential equations consists of a set of equations that simultaneously relate one or more unknown functions and their first derivatives with respect to the same independent variable.
NOTE: The first derivatives are those of order 1, while the independent variable is usually t, which indicates time, or x.
These differential equations are so called because only the first derivative of each variable appears. They are used to build scientific models and write them mathematically, or they are very useful in qualitative analysis, especially in equilibrium or stability studies.
Conclusions
We can conclude by saying that a differential equation is a kind of mathematical rule that informs us how something is changing. For example, a differential equation doesn't tell us that the temperature is 20°C, but it provides us with the information that the temperature is increasing by 2°C every hour.
Question
Did you know that the founding fathers of differential equations were Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz?
Did you know that between the two, it was Leibniz who coined the term aequatio differentialis and used the notation γx, γy?

ITALIAN

15-07-2025 - Analisi Matematica - Equazioni differenziali [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X-47-46-45)
Equazioni differenziali

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Le equazioni differenziali sono un particolare strumento matematico. Possiamo dire che servono per dirci come cambiano le cose nel tempo. Le equazioni differenziali sono un modo per descrivere i cambiamenti. Vengono usate per descrivere il cambiamento nei moti dei corpi, in elettromagnetismo, in termodinamica, in biologia, in economie e anche nella finanza.
Equazione differenziale, spiegazione tecnica
Un’equazione differenziale ordinaria di ordine n per y(t) è un’equazione in cui compaiono una variabile indipendente t, la funzione (incognita) y(t) e le derivate, al più di ordine n, della funzione y(t).
La sua forma generale è la seguente:
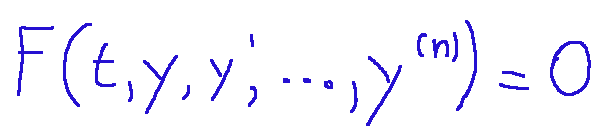
Ogni funzione y(t) derivabile n volte in un intervallo aperto I che rende l'equazione identicamente verificata (cioè verificata per ogni t appartenente a I) si dice soluzione o integrale generale dell'equazione.
NOTA: Un equazione differenziale ordinaria può avere esattamente una soluzione, infinite soluzioni oppure nessuna soluzione.
Equazione differenziale ordinaria lineare del primo ordine
Prendiamo come esempio la seguente equazione:
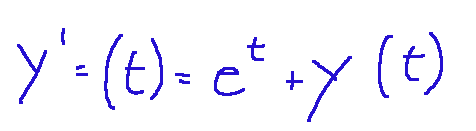
questa è un equazione differenziale del primo ordine in quanto la funzione incognita vi compare derivata una volta. In questo caso la variabile indipendente è t e si usa indicare l'equazione anche nella seguente forma semplificata:
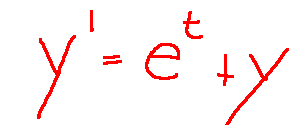
considerazioni riguardo all'equazione precedente
Il tipo di equazione è lineare, di primo ordine e a coefficienti costanti.
Avendo un dato iniziale si può determinare la costante (C) e ottenere l'unica soluzione che passa per quel punto.
L'integrale generale
Prendiamo come esempio la seguente equazione differenziale e cerchiamo l'integrale generale.
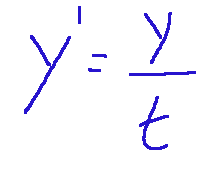
Senza eseguire i vari passaggi mostro qui di seguito l'integrale generale dell'equazione differenziale qui sopra riportata:
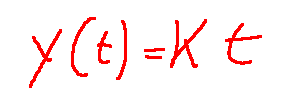
L'integrale generale di un equazione differenziale è la forma con tutte le costanti che descrive tutte le soluzione. Infatti nell'esempio di prima abbiamo il termine k che rappresenta la costante.
Sistemi di equazioni differenziali del primo ordine
Qui di seguito trovate un esempio di un sistema di equazioni differenziali del primo ordine in forma normale:
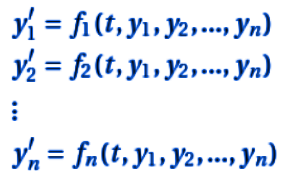
Un sistemi di equazioni differenziali del primo ordine consiste in un pacchetto di equazioni che legano simultaneamente una o più funzioni incognite e le loro derivate prime rispetto alla stessa variabile indipendente.
NOTA: Le derivate prime sono quelle di ordine 1, mentre la variabile indipendente di solito è t, che indica il tempo, oppure x.
Queste equazioni differenziali vengono chiamate così perché compare solo la derivata prima di ciascuna variabile. Esse servono per costruire dei modelli scientifici e scriverli in forma matematica oppure sono molto utili nell'analisi qualitativa, soprattutto negli studi degli equilibri o di stabilità.
Conclusioni
Possiamo concludere dicendo che un equazione differenziale è una sorta di regola matematica che ci informa su come qualcosa sta cambiando. Facciamo un esempio, un equazione differenziale non dice che la temperatura è di 20°, ma ci fornisce l'informazione che la temperatura sta aumentando di 2 gradi ogni ora.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che i padri fondatori delle equazioni differenziali furono Isaac Newton e Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz?
Lo sapevate che tra i due a coniare il termine aequatio differentialis ed ad usare la notazione 𝑑x, 𝑑y fu proprio Leibniz?
THE END