
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

08-05-2025 - Physics - Properties of the magnetic field [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_37-)
Properties of the magnetic field

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Properties of the magnetic field
The properties of a magnetic field are 7 and below we can see them all listed:
-Intensity and direction
-Lines of force
-Origin of the magnetic field
-Force on a moving charge
-Field solenoidal
-Interaction with materials
-Electromagnetic induction
Remember that a magnetic field is a vector and that in the international system it is measured in Tesla.
What does it mean that a magnetic field is 1 Tesla?
It means that the intensity of the magnetic field is such that it exerts a force of 1 newton on a charge of 1 coulomb that moves at 1 meter per second perpendicular to the field itself.
Below is what we just said described mathematically:
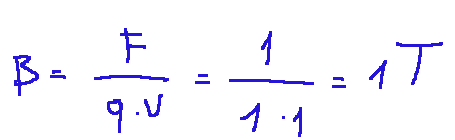
The magnetic field flux
The magnetic field flux is a physical quantity. It measures the quantity of magnetic field that passes through a surface.
Here is its mathematical expression:
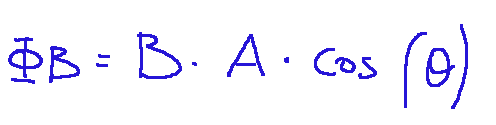
Where:
Φ𝐵 = magnetic flux
B = intensity of the magnetic field
A = area of the surface crossed
θ = angle between the magnetic field and the normal to the surface
Maxwell's second law
Maxwell's second law is also known as Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
We can summarize the concept of this law as follows. A magnetic field varying in time generates an induced electric field. We could stop here to avoid making things complicated, but we absolutely must say that this electric field is non-conservative and can create a current in a closed circuit.
Below I report the mathematical formula that derives from Maxwell's second law.
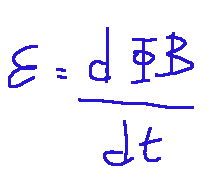
Where:
ε = electromotive force induced in a closed circuit
This formula expresses the concept that when the magnetic flux changes over time, a circulating electric field is generated. A circulating electric field is an electric field that follows closed trajectories, that is, the field lines form loops.
And here comes the fun part because a circulating electric field induces an electric current in a closed conductor, for example in a coil or in a wire.
Maxwell's fourth law
Maxwell's fourth law is an extension of Ampere's original law.
This law says that a circulating magnetic field can be generated by two things:
1-A real electric current, such as a wire carrying current
2-A variation in time of an electric field, so a circulating magnetic field can be generated even without wires or charges.
I consider Maxwell's fourth law one of the most interesting things in the field of the properties of magnetic fields because it states that a circulating magnetic field can be generated even in the absence of wires or moving charges, as long as there is an electric field that varies over time.
Diamagnetic substances
In the field of magnetic fields we talk about diamagnetic substances when a material, in which an external magnetic field is applied, generates an induced magnetic field in the opposite direction.
Paramagnetic substances
We speak of paramagnetic substances when these materials, immersed in an external magnetic field, become weakly magnetized in the same direction.
Ferromagnetic substances
Finally we have ferromagnetic substances, perhaps the most fascinating. These are materials that can become strongly magnetized and maintain the magnetization even after the external magnetic field has been removed
Biot-Savart Law
Just rewriting the Biot-Savart law is painful for me, but now I'm regaining my strength and I've reported its mathematical expression below:
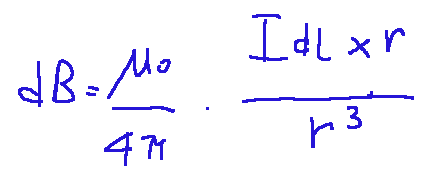
This law is fundamental in the field of magnetic fields and electromagnetism.
It describes the magnetic field generated by an electric current in a conductor.
Essentially, this law allows you to calculate the magnetic field at any point in space starting from the distribution of the current.
Conclusions
The magnetic field is one of the fundamental forces of nature and has two very important properties:
-It can create interaction with electric currents.
-The variation of the magnetic flux over time can generate an induced electromotive force
Question
In this article I described what diamagnetic details are. Did you know that in 1997 the physicist Andre Geim managed to levitate a live frog with a magnetic field? This is possible because the frog is diamagnetic.

ITALIAN

08-05-2025 - Fisica - Proprietà del campo magnetico [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_37-)
Proprietà del campo magnetico

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Proprietà del campo magnetico
Le proprietà di un campo magnetico sono 7 e qui di seguito le possiamo vedere tutte elencate:
-Intensità e direzione
-Linee di forza
-Origine del campo magnetico
-Forza su una carica in movimento
-Campo solenoidale
-Interazione con materiali
-Induzione elettromagnetica
Ricordiamo che un campo magnetico è un vettore e che nel sistema internazionale si misura in Tesla.
Cosa vuol dire che un campo magnetico vale 1 Tesla?
Significa che l’intensità del campo magnetico è tale da esercitare una forza di 1 newton su una carica di 1 coulomb che si muove a 1 metro al secondo perpendicolarmente al campo stesso.
Qui di seguito quello che abbiamo appena detto descritto matematicamente:
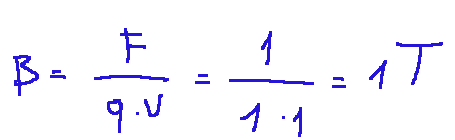
Il flusso del campo magnetico
Il flusso del campo magnetico è una grandezza fisica. Esso misura la quantità di campo magnetico che attraversa una superficie.
Qui di seguito la sua espressione matematica:
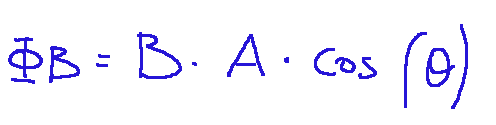
Dove:
Φ𝐵 = flusso magnetico
B = intensità del campo magnetico
A = area della superficie attraversata
θ = angolo tra il campo magnetico e la normale alla superficie
La seconda legge di Maxwell
La seconda legge di Maxwell è conosciuta anche come la legge di Faraday dell’induzione elettromagnetica.
Possiamo sintetizzare il concetto di questa legge, come segue. Un campo magnetico variabile nel tempo genera un campo elettrico indotto. Potremmo anche fermarci qui per non rendere le cose complicate, ma dobbiamo assolutamente dire che questo campo elettrico è non conservativo e può creare una corrente in un circuito chiuso.
Qui di seguito riporto la formula matematica che deriva dalla seconda legge di Maxwell.
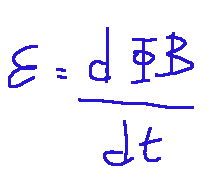
Dove:
ε = forza elettromotrice indotta in un circuito chiuso
Questa formula esprime il concetto che quando il flusso magnetico cambia nel tempo si genera un campo elettrico circolante. Un campo elettrico circolante è un campo elettrico che segue traiettorie chiuse, ovvero le linee di campo formano anelli.
E qui viene il bello perchè un campo elettrico circolante induce una corrente elettrica in un conduttore chiuso, ad esempio in una spira o in un filo.
La quarta legge di Maxwell
La quarta legge di Maxwell è un'estensione della legge originale di Ampere.
Questa legge dice che un campo magnetico circolante può essere generato da due cose:
1-Una corrente elettrica reale, come un filo percorso da corrente
2-Una variazione del tempo di un campo elettrico, quindi un campo magnetico circolante può essere generato anche senza fili o cariche.
Ritengo la quarta legge di Maxwell una delle cose più interessanti nell’ambito delle proprietà dei campi magnetici perché afferma che un campo magnetico circolante può essere generato anche in assenza di fili o cariche in movimento, basta che ci sia un campo elettrico variabile nel tempo.
Le sostanze diamagnetiche
Nell’ambito dei campi magnetici parliamo di sostanze diamagnetiche quando un materiale, in cui viene applicato un campo magnetico esterno, si genera un campo magnetico indotto in direzione opposta.
Le sostanze paramagnetiche
Parliamo di sostanze paramagnetiche quando questi materiali, immersi in un campo magnetico esterno, si magnetizzano debolmente nella stessa direzione.
Le sostanze ferromagnetiche
Infine abbiamo le sostanze ferromagnetiche, forse quelle più affascinanti. Queste sono materiali che possono magnetizzarsi fortemente e mantenere la magnetizzazione anche dopo che il campo magnetico esterno è stato rimosso
Legge di Biot-Savart
Solo riscrivere la legge di Biot-Savart mi viene male, ma ora riprendo le forze e qui sotto riporto la sua espressione matematica:
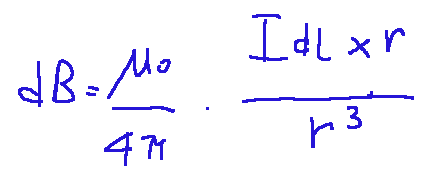
Questa legge è fondamentale nell’ambito dei campi magnetici e dell'elettromagnetismo.
Essa descrive il campo magnetico generato da una corrente elettrica in un conduttore.
Sostanzialmente questa legge permette di calcolare il campo magnetico in qualsiasi punto dello spazio a partire dalla distribuzione della corrente.
Conclusioni
Il campo magnetico è una delle forze fondamentali della natura e possiede due proprietà molti importanti:
-Può creare interazione con le correnti elettriche.
-La variazione del flusso magnetico nel tempo può generare una forza elettromotrice indotta
Domanda
In questo articolo ho descritto cosa sono i particolari diamagnetici. Lo sapevate che nel 1997 il fisico Andre Geim riuscì a far levitare una rana viva con un campo magnetico? Questo è possibile perché la rana è diamagnetica.
THE END
