~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

04-06-2025 - System Analysis - Dynamic System [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a short instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_93)
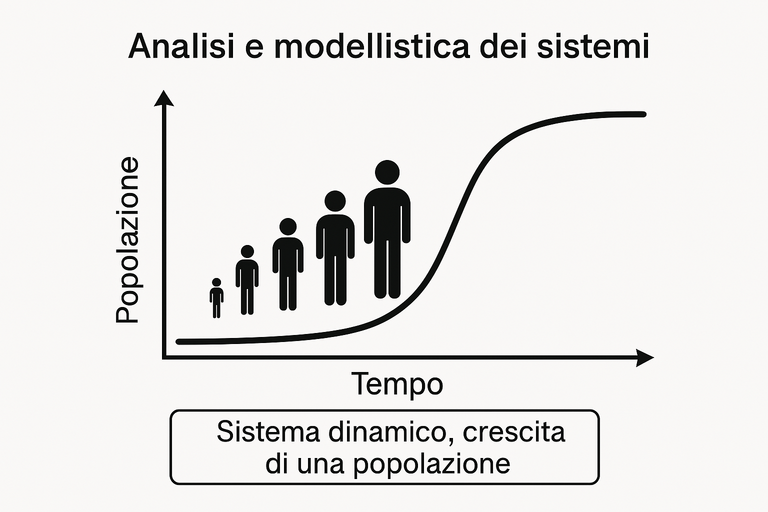
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Static system, system dynamic
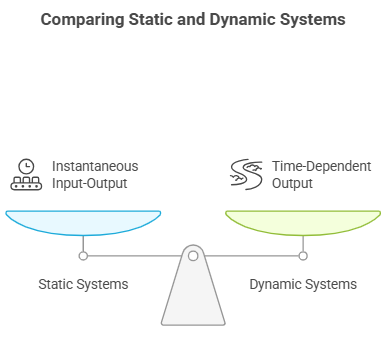
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is napkin.ai
In systems analysis, systems are classified into two broad categories: static systems and dynamic systems.
A static system is defined as such when the input-output relationship is instantaneous, that is, the value of the output depends only on the value of the input.
A dynamic system is defined as such when the value of the output at a time t depends on the value assumed by the input in all previous times of t.
Note: A static system can be seen as a dynamic system without state variables
Note 2: In ideal conditions, an example of a static system can be a resistor. In ideal conditions, a resistor is an example of a static system because its output, i.e. the voltage across the resistor, depends only on the input, i.e. the current that passes through it, and this in an instantaneous way.
Note 3: An example of a dynamic system can be a capacitor or an inductor, in fact a dynamic system is a system that also depends on the past, i.e. it has memory. In a capacitor, the current depends on the variation of the voltage over time and this is a typical dynamic behavior
Dynamic behavior
The way in which a system evolves is called behavior. The dynamic behavior of a system is the way in which a system evolves in response to inputs or initial conditions, taking into account the internal interactions between its components.
A dynamic system has typical characteristics:
Stationarity
Response time
Oscillations
Stability
An intuitive example of a system with dynamic behavior could be that of a water tank with a tap and a drain. In this type of system, if we open the tap, the water level begins to rise. In this case, the dynamic behavior describes how and how quickly the level rises or stabilizes as a function of the amount of water that enters and exits. In the previous lines, in fact, we said that a dynamic system has several typical characteristics, one of which is stationarity, that is, the ability to reach an equilibrium after a certain time.
Finite State System
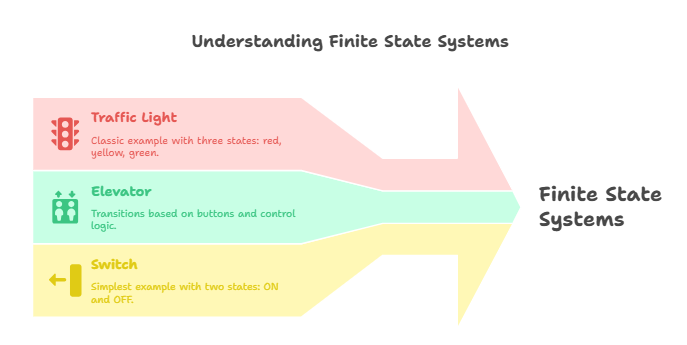
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is napkin.ai
A finite state system is a system in which the state space has finite elements.
NOTE: What is state space?
Each state is a complete configuration of the variables that describe the system at a certain instant and the state space is the set of all possible states in which a system can be at a given time.
examples of finite state systems
-1-Traffic light
The traffic light is the most classic example, it has only three states, it can be red, yellow or green.
-2-Elevator
Transitions occur based on the buttons pressed and the control logic and the possible states are the number of stops that the elevator can make.
-3-
The simplest example is that of the switch. It has only two states, ON and OFF
Forced evolution
Forced evolution represents the response of the system when its initial state is null, i.e. without initial conditions, and is prompted exclusively by an external forcing input.
We can say that the forced evolution of a system is the response that occurs starting from a null state, and as a consequence of a forcing input
Equilibrium
The equilibrium point of a system is a point in which the system has no evolution in the state.
If a system is perturbed it could lose its equilibrium, but a subsequent evolution of the system could bring the system back to its equilibrium point.
Conclusions
Dynamic systems depend on time, memory of the past, stability, behavior, mathematical modeling. Examples include: a pendulum, an RLC circuit, population growth. Imagine how important it can be to understand the evolution of a system if we are talking about population growth.
Question
We said that population growth is a dynamic system.
Did you know that the World Population Prospects analyzes global demographic trends and provides forecasts up to 2100? Did you know that this study would have identified that in 2050 there will be more elderly people than children?

ITALIAN

04-06-2025 - Analisi dei sistemi - Sistema dinamico [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_93)

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Sistema statico, sistema dinamico

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è napkin.ai
In analisi dei sistemi, i sistemi vengono classificati in due grandi categorie: sistemi statici e sistemi dinamici.
Un sistema statico è definito tale quando il legame ingresso-uscita è istantaneo, cioè il valore dell’uscita dipende solo dal valore dell’ingresso.
Un sistema dinamico viene definito tale quando il valore dell’uscita ad un istante t dipende dal valore assunto dall’ingresso in tutti gli istanti precedenti di t.
Nota: Un sistema statico può essere visto come un sistema dinamico senza variabili di stato
Nota 2: In condizioni ideali, è un esempio di sistema statico può essere una resistenza. In condizioni ideali, una resistenza è un esempio di sistema statico perché la sua uscita, cioè la tensione ai capi della resistenza, dipende solo dall'ingresso, cioè dalla corrente che la attraversa, e questo in modo istantaneo.
Nota 3: Un esempio di sistema dinamico possono essere un condensatore o un'induttanza, infatti un sistema dinamico è un sistema che dipende anche dal passato, ovvero ha memoria. In un condensatore la corrente dipende dalla variazione della tensione nel tempo e questo è un tipico comportamento dinamico
Il comportamento dinamico
Il modo in cui un sistema si evolve viene chiamato comportamento. Il comportamento dinamico di un sistema è il modo in cui un sistema evolve in risposta a ingressi o condizioni iniziali, tenendo conto delle interazioni interne tra le sue componenti.
Un sistema dinamico ha delle caratteristiche tipiche:
Stazionarietà
Tempo di risposta
Oscillazioni
Stabilità
Un esempio intuitivo di un sistema con un comportamento dinamico potrebbe essere quello di un serbatoio d’acqua con un rubinetto ed uno scarico. In questa tipologia di un sistema, se apriamo il rubinetto, il livello dell’acqua comincia a salire. In questo caso, il comportamento dinamico descrive come e quanto velocemente il livello sale o si stabilizza in funzione della quantità d’acqua che entra ed esce. Nelle righe prima infatti abbiamo detto che un sistema dinamico ha diverse caratteristiche tipiche, di cui una è la stazionarietà, cioè la capacità di raggiungere un equilibrio dopo un certo tempo.
Sistema a stati finiti

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è napkin.ai
Un sistema a stati finiti è un sistema in cui lo spazio di stato ha finiti elementi.
NOTA: Cosa è lo spazio di stato?
Ogni stato è una configurazione completa delle variabili che descrivono il sistema in un certo istante e lo spazio di stato è l’insieme di tutti i possibili stati in cui un sistema può trovarsi in un dato momento.
esempi di sistemi a stati finiti
-1-Semaforo
Il semaforo è il più classico degli esempi, esso a solo tre stati, può essere rosso, giallo o verde.
-2-Ascensore
Le transizioni avvengono in base ai pulsanti premuti e alla logica di controllo e gli stati possibili sono il numero delle fermate che può fare l'ascensore.
-3-
L'esempio più semplice è quello dell'interruttore. Esso ha solo due stati, ON e OFF
Evoluzione forzata
L'evoluzione forzata rappresenta la risposta del sistema quando il suo stato iniziale è nullo, ossia privo di condizioni iniziali, e viene sollecitato esclusivamente da un ingresso esterno di forzamento.
Possiamo dire che L'evoluzione forzata di un sistema è la risposta che si ha a partire da stato nullo, e in conseguenza di un ingresso di forzamento
L'equilibrio
Il punto di equilibrio di un sistema è un punto nel quale il sistema non ha evoluzione nello stato.
Se un sistema è perturbato potrebbe perdere l'equilibrio, ma una successiva evoluzione del sistema, potrebbe riportare il sistema al suo punto di equilibrio.
Conclusioni
I sistemi dinamici dipendono dal tempo, dalla memoria del passato, dalla stabilità, dal comportamento, da una modellazione matematica. Degli esempi possono essere: il pendolo, un circuito elettrico RLC, la crescita di una popolazione. Immaginate quanto possa essere importante capire l'evoluzione di un sistema se parliamo proprio della crescita di una popolazione.
Domanda
Abbiamo detto che la crescita di una popolazione è un sistema dinamico.
Sapevate che il World Population Prospects analizza le tendenze demografiche globali e fornisce previsioni fino al 2100? Sapevate che questo studio avrebbe individuato che nel 2050 ci saranno più anziani che bambini?
THE END
