~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
04-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - VSEPR Model [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_90)
VSEPR Model
Previews
In chemistry today we have experimental methods that allow us to know both the bond distance (d) and the bond angle (α)
Where:
bond distance (d) = distance between the nuclei of two atoms bound in a molecule

the bond angle (α) = is the signed angle between two covalent bonds that start from the same atom. This angle influences the shape and geometry of the molecules.
Covalent bond = type of chemical bond in which two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to reach a more stable electronic configuration. This bond is formed mainly between non-metallic atoms with similar electronegativity.
What is the VSEPR Model
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory, also known as VSEPR, is a theoretical model used to predict the bond angle of molecules.
For example, if we take a water molecule, i.e. H2O, the bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom is approximately 104.5°. This particular bond of the water molecule gives it its characteristic "V" shape
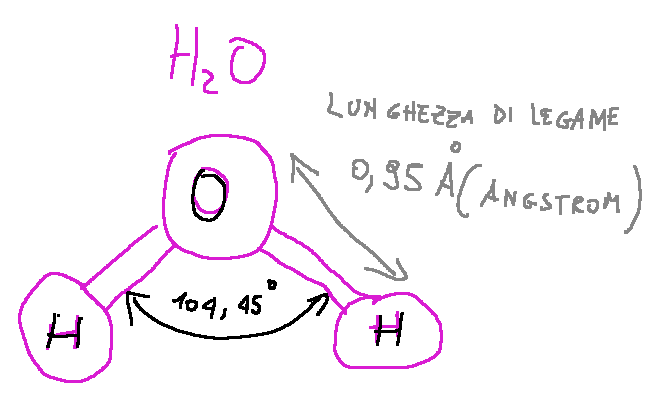
Where:
H = hydrogen
O = oxygen
According to the VSEPR model, an atom has an approximately spherical electronic charge distribution, but when it enters a bond, it redistributes its spherical charge density in defined directions of space. These are the bond directions. These areas arrange themselves at the maximum possible distance, or greatest possible bond angle, due to repulsion. The pairs involved in the covalent bond, also called CL bond pairs, and the non-bonding pairs, also called CS lone pairs, are regions of space with a high density of negative charge.
We can deduce that the geometry of the bonds around a central atom depends on the number of CL (covalent bonds) and the number of lone pairs (CS) that are arranged in the space furthest away.
Electrostatics
Electrostatics tells us that equal charges, free to move in a sphere, and constrained at the center of this sphere, arrange themselves so as to minimize their repulsion, at the maximum distance.

Molecular geometry
By studying the number of bonds (Lewis theory) and using the VSEPR model to identify the bond angle we can trace the molecular geometry.
in other words
Molecular geometry defines the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. Through molecular geometry we can determine different physical and chemical properties of molecules. We can determine polarity, reactivity and state of aggregation.
The intermolecular forces that determine both the physical properties and the state of aggregation depend on the polarity of the molecules.
I remember that intermolecular forces are electrostatic in nature.
Note: The greater the μ (polarity) of a molecule, the greater the attractive forces between the molecules.
Multiple Bonds
The electron pairs in a multiple bond occupy only one direction in space and therefore, for the purposes of the geometry of the molecule, it behaves like a single bond.
A multiple bond can be, for example, a double bond or a triple bond.
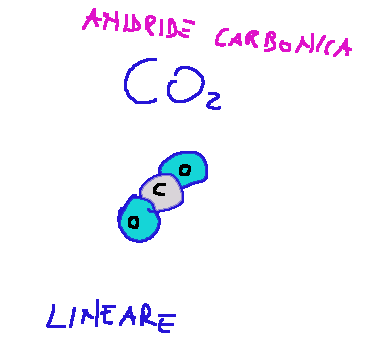
Where:
C = carbon
O = oxygen
Conclusions
The VSEPR model is used to identify the geometry of molecules based on the repulsion that occurs between electron pairs around a central atom.
Molecular geometry is the arrangement of atoms after they have formed a molecule. It influences many physical and chemical properties of molecules themselves.
Question
Do you remember studying the geometry of molecules? Do you remember studying how hydrogen atoms are arranged around the oxygen atom in a water molecule?

[ITALIAN]
04-03-2025 - Basi di chimica - Modello VSEPR [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_90)
Modello VSEPR
Anticipazioni
In chimica oggi abbiamo dei metodi sperimentali che permettono di conoscere sia la distanza di legame (d) che l'angolo di legame (α)
Dove:
distanza di legame (d) = distanza tra i nuclei di due atomi legati in una molecola

l'angolo di legame (α) = è l'angolo firmato tra due legami covalenti che partono dallo stesso atomo. Questo angolo influenza la forma e la geometria delle molecole.
Legame covalente = tipo di legame chimico in cui due atomi condividono una o più coppie di elettroni per raggiungere una configurazione elettronica più stabile. Questo legame si forma principalmente tra atomi non metallici e con elettronegatività simile.
Cosa è il Modello VSEPR
La teoria Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion, detta appunto VSEPR è un modello teorico usato per prevedere l'angolo di legame delle molecole.
Per esempio se prendiamo una molecola di acqua, cioè H2O, l'angolo di legame tra i due atomi di idrogeno e l'atomo di ossigeno è di circa 104,5°. Questo particolare legame della molecola dell'acqua da a questa la sua caratteristica forma a "V"

Dove:
H = idrogeno
O = ossigeno
Secondo il modello VSEPR un atomo ha una distribuzione di carica elettronica approssimativamente sferica, ma quando entra a far parte di un legame, ridistribuisce la sua densità di carica sferica in definite direzioni dello spazio. Queste sono le direzioni dei legami. Queste zone si dispongono alla massima distanza possibile, ovvero maggior angolo di legame possibile, per effetto della repulsione. Le coppie coinvolte nel legame covalente, dette anche coppie di legame CL, e le coppie di non legame, dette anche coppie solitarie CS, sono zone dello spazio ad alta densità di carica negativa.
Possiamo dedurre che la geometria dei legami attorno ad un atomo centrale dipende dal numero di CL (legami covalenti) e dal numero di coppie solitarie (CS) che si dispongono nello spazio il più lontano.
L'elettrostatica
L'elettrostatica ci dice che le cariche uguali, libere di muoversi in una sfera, e vincolate al centro di questa sfera, si dispongono in modo da minimizzare la loro repulsione, alla distanza massima.

Geometria molecolare
Studiando il numero di legami (teoria di Lewis) ed utilizzando il modello VSEPR per identificare l'angolo di legame possiamo risalire alla geometria molecolare.
in altre parole
La geometria molecolare definisce la disposizione tridimensionale degli atomi all'interno di una molecola. Tramite la geometria molecolare possiamo determinare diverse proprietà fisiche e chimiche delle molecole. Possiamo determinare la polarità, la reattività e lo stato di aggregazione.
Dalla polarità delle molecole dipendono le forze intermolecolari che determinano sia le proprietà fisiche che lo stato di aggregazione.
Ricordo che le forze intermolecolari sono di natura elettrostatica.
Nota: Quanto maggiore è μ (polarità) di una molecola tanto maggiori sono le forze di attrazione fra le molecole.
Legami multipli
Le coppie di elettroni in un legame multiplo occupano una sola direzione nello spazio e quindi, al fine della geometria della molecola, si comporta come un legame singolo.
Un legame multiplo può essere ad esempio un doppio legame o un triplo legame.

Dove:
C = carbonio
O = ossigeno
Conclusioni
Il modello VSEPR è utilizzato per identificare la geometria delle molecole sulla base della repulsione che avviene tra le coppie di elettroni attorno a un atomo centrale.
La geometria molecolare è la disposizione che hanno gli atomi dopo che hanno formato una molecola. Essa influenza molte proprietà fisiche e chimiche delle molecole stesse.
Domanda
Vi ricordate di aver studiato la geometria delle molecole? Vi ricordate di aver studiato come si dispongono gli atomi di idrogeno attorno all'atomo di ossigeno in una molecola d'acqua?
THE END