~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
01-02-2024 - Physics - Conduction of a plate [EN]-[IT]
Conducting a plate
Basic concepts
Entropy in thermodynamics is represented with the letter S and is an extensive quantity, furthermore it is a state function.
For S we must take into account the following postulates:
-S = S(m,V,U)
-it is additive
-has production >=0
-in an isolated system the state of equilibrium that is reached by eliminating an internal constraint is such as to maximize the entropy, compatibly with the other constraints of the system.
Temperature graph of a flat plate
The drawing below shows a plate.
The red line and the dotted line show the temperature distributed across it.
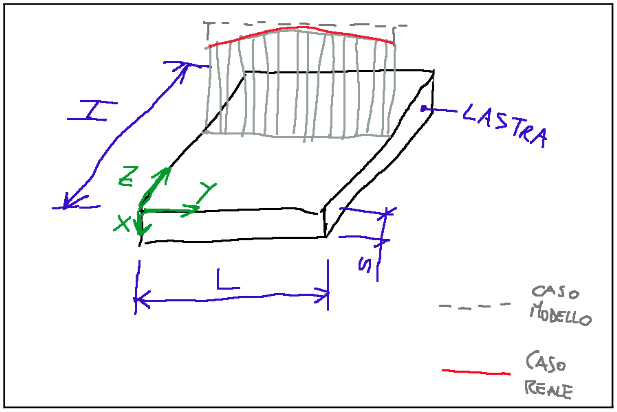
We note that the dotted line is homogeneous, while the red line lowers on the edges, that is, the temperature decreases as we approach the external perimeter of the plate. The dotted line shows the temperature of the plate in a model case, while the red line in a real case.
In the real case we have the so-called edge effect, that is, the temperature on the plate is almost constant everywhere, except near the edge.
Conditions taken as reference
There will be two conditions that must be taken into consideration for the study of the plate:
-the initial condition
-the boundary condition
The initial condition
The plate will be exposed near a heat source and at this moment the phenomenon of thermal conduction will begin.
The initial condition is the condition that occurs when the conductive phenomenon begins and represents how the temperature is distributed in the plate at this very moment.
The boundary conditions
As we described before, at the edges of the plate there are phenomena that alter the temperature significantly. Boundary conditions are those conditions that describe the temperature at the edges of the plate.
Boundary conditions can be evaluated via two approaches:
-Fixed temperature condition
-Flow condition fixed
-Convective boundary condition
- Radiative boundary condition
Below is a brief description of these four assessments:
In the fixed temperature condition it is assumed that at every instant the temperature on one of the two sides of the plate is known.
In the fixed flow condition, the tangent of the temperature with respect to space is considered known
In the convective boundary condition, the convective motion of the fluid or gas that is near the plate is examined. This motion can determine internal energy transport. Convection can occur in two ways, forced or natural.
In the radiative boundary condition, another heat transmission mechanism, thermal radiation, is considered. In this case, a transfer of internal energy occurs from the body at a higher temperature to the body at a lower temperature
Conclusions
To study how the temperature changes in a body that is subjected to thermal conduction we must consider the initial condition and the boundary conditions.
Request
Have you studied thermal conduction in the past?

01-02-2024 - Fisica - Conduzione di una lastra [EN]-[IT]
Conduzione di una lastra
Concetti base
L'entropia nella termodinamica è rappresentata con la lettera S ed è una grandezza estensiva, inoltre essa è una funzione di stato.
Per S dobbiamo tenere conto quanto dei seguenti postulati:
-S = S(m,V,U)
-è additiva
-ha produzione >=0
-in un sistema isolato lo stato di equilibrio che si raggiunge eliminando un vincolo interno, è tale da rendere massima l'entropia, compatibilmente con gli altri vincoli del sistema.
Grafico della temperatura di una lastra piana
Nel disegno qui sotto è rappresentata una lastra.
La riga rossa e la riga tratteggiata mostrano la temperatura distribuita su di essa.

Notiamo che la riga tratteggiata è omogenea, mentre la riga rossa si abbassa sui bordi, cioè la temperatura diminuisce quando ci avviciniamo al perimetro esterno della lastra. La riga tratteggiata mostra la temperatura della lastra in un caso modello, mentre la riga rossa in un caso reale.
Nel caso reale abbiamo il cosiddetto effetto bordo, cioè la temperatura sulla lastra è quasi ovunque costante, tranne che nelle vicinanze del bordo.
Condizioni prese in riferimento
Le condizioni che dovranno essere prese in esame per lo studio della lastra saranno due:
-la condizione iniziale
-la condizione al contorno
La condizione iniziale
La lastra verrà esposta vicino ad una fonte di calore ed in questo momento inizierà il fenomeno della conduzione termica.
La condizione iniziale è la condizione che si verifica nel momento in cui inizia il fenomeno conduttivo e rappresenta come si distribuisce la temperatura nella lastra proprio in questo istante.
Le condizioni al contorno
Come abbiamo descritto prima, ai bordi della lastra esistono dei fenomeni che alterano la temperatura in maniera consistente. Le condizioni al contorno sono quelle condizioni che descrivono la temperatura nei bordi della lastra.
Le condizioni al contorno possono essere valutate tramite due approcci:
-Condizione di temperatura fissata
-Condizione di flusso fissato
-Condizione al contorno di tipo convettivo
-Condizione al contorno di tipo radiativo
Qui di seguito una breve descrizione di queste quattro valutazioni:
Nella condizione di temperatura fissata si suppone che ad ogni istante è nota la temperatura su uno dei due lati della lastra.
Nella condizione di flusso fissata si considera nota la tangente della temperatura rispetto allo spazio
Nella condizione al contorno di tipo convettivo viene preso in esame il moto convettivo del fluido o di un gas che è nei pressi della piastra. Questo moto può determinare un trasporto di energia interna. La convezione può avvenire in due modi, forzata o naturale.
Nella condizione al contorno di tipo radiativo viene considerato un altro meccanismo di trasmissione del calore, l'irraggiamento termico. In questo caso avviene un trasferimento di energia interna dal corpo a temperatura maggiore verso quello a temperatura minore
Conclusioni
Per studiare come si modifica la temperatura in un corpo che viene sottoposto ad una conduzione termica dobbiamo considerare la condizione iniziale e le condizioni al contorno.
Domanda
Avete studiato in passato la conduzione termica?
THE END






