
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

12-04-2025 - Physics - Rigid body equilibrium [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_74)
Rigid body equilibrium

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
The rigid body
The rigid body is a system of material points in which the distances between all possible pairs of points cannot vary. Examples of rigid bodies can be a billiard ball, a wheel, a spinning top, etc.
We can also define a rigid body as follows. A rigid body is an ideal model of an object in which the distances between all its parts remain constant. All this regardless of the forces applied. We can create a further synthesis of what has just been said and say that a rigid body is an object that does not deform under the action of external forces.
The main characteristics of a rigid body are the following:
-The particles that make up the body always maintain the same distance from each other
-A rigid body does not undergo compression, stretching or torsion.
-A rigid body can rotate and translate in space. When a rigid body does this it occurs without any change in its internal structure.
When studying the motion of a rigid body we realize that the various points can describe different trajectories.
In general, the motion of a rigid body turns out to be a composition of a rigid translation, which can be represented by the translation of its center of mass and a rotation around an axis.
Cardinal equations
The two cardinal equations describe the dynamics of a rigid body.
Cardinal equation of momentum
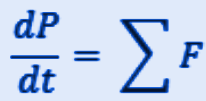
Cardinal equation of angular momentum
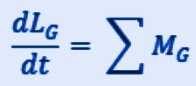
Density
In general, when studying rigid bodies they are considered as continuous bodies in which the mass is considered to be uniformly distributed inside the entire volume.
the total mass corresponds to the sum of the infinitesimal masses dm that compose the volume. The symbol 𝛒 indicates the density (or volumetric mass), which uniquely defines the distribution of mass in space and is equal to the ratio between dm and dV. In particular, we will say that the density is constant throughout the volume (𝛒=M/V), when the body is homogeneous.
The center of mass corresponds to the geometric center of the body. This means that a homogeneous rigid body that forms a volume with some symmetry will have its center of mass in the center of symmetry of the occupied volume.
We can summarize by saying that in physics, density is a quantity that expresses the ratio between the mass of a body and its volume. Technically, it means the following. Density indicates how much material is contained in a certain space.
examples
iron, for example, is an object with high density while wood is an object with low density. Objects with high density are more compact than those with low density.
Here is the formula for the density of a body:
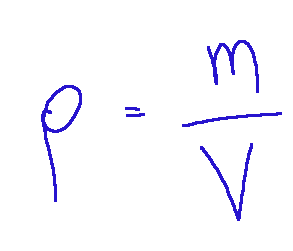
Equilibrium of the rigid body
The natural movement of a rigid body is a roto-translational motion, therefore the equilibrium condition of the system is given by the fact that it can neither translate nor rotate.
We must keep these two characteristics in mind:
-in order for it not to translate, the vector sum of all the external forces applied to it must be zero;
-in order for it not to rotate, the sum of all the torsional moments of the forces applied to it, calculated with respect to any pole, must be zero.
We can say that the rigid body will have constant total momentum and angular momentum.
We can summarize the equilibrium of the rigid body by saying that it occurs when the forces and moments applied to it balance each other.
This particular condition thus prevents any translational or rotational movement. There can be different types of equilibria. In fact, there is static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium, translational equilibrium and rotational equilibrium.
Center of gravity of a rigid body

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
After talking about the rigid body, its equilibrium and density, now let's talk about the center of gravity of a rigid body.
The center of gravity of a rigid body is the point where all the mass of the body can be considered concentrated to facilitate the study of its motion.
The center of gravity is also the point where the weight force of the body acts as if it were applied to a single point.
The center of gravity has several properties, below we list two:
-The center coincides with the geometric center if a body is homogeneous and has a symmetrical shape. An example of these shapes can be the sphere and the cube.
-if a body has an irregular distribution of mass, the center of gravity depends on the arrangement of the different parts.
We can say that the center of gravity is fundamental for studying the equilibrium of the rigid body, because the body will tend to rotate around this point under the action of external forces.
Today we can say that calculating the center of gravity of a very complex geometric shape is not that difficult because if we manage to recreate the three-dimensional model of this shape, the three-dimensional modeling software will then provide us with the exact point where the center of gravity of the drawn mass is located.
Conclusions
In conclusion, understanding and studying rigid bodies well is important because it allows us to simplify and better understand the behavior of real objects in the world around us and to design the objects we use daily.
Question
The concept of a rigid body does not have a single inventor, however we can say that in the 17th century there were studies that we can define as the first key studies of the modern concept of a rigid body. Did you know that these studies were done by Isaac Newton himself?

ITALIAN

12-04-2025 - Fisica - Equilibrio del corpo rigido [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_74)
Equilibrio del corpo rigido

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Il corpo rigido
Il corpo rigido è un sistema di punti materiali in cui le distanze tra tutte le possibili coppie di punti non possono variare. Esempi di corpo rigido possono essere una sfera da biliardo, una ruota, una trottola, ecc.
Possiamo definire un corpo rigido, anche come segue. Un corpo rigido è un modello ideale di un oggetto in cui le distanze tra tutte le sue parti rimangono costanti. Tutto questo indipendentemente dalle forze applicate. Possiamo creare un ulteriore sintesi di quanto appena detto e dire che un corpo rigido è un oggetto che non si deforma sotto l’azione di forze esterne.
Le principali caratteristiche di un corpo rigido sono le seguenti:
-Le particelle che compongono il corpo mantengono sempre la stessa distanza tra loro
-Un corpo rigido non subisce compressioni, stiramenti o torsioni.
-Un corpo rigido può ruotare e traslare nello spazio. Quando un corpo rigido fa questo avviene senza alcun cambiamento nella sua struttura interna.
Quando si studia il moto di un corpo rigido ci si rende conto che i vari punti possono descrivere traiettorie diverse.
In generale, il moto di un corpo rigido risulta essere una composizione di una traslazione rigida, che può essere rappresentata dalla traslazione del suo centro di massa ed una rotazione intorno ad un asse.
Equazioni cardinali
Le due equazioni cardinali descrivono la dinamica di un corpo rigido.
Equazione cardinale della quantità di moto
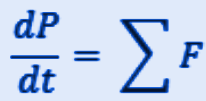
Equazione cardinale del momento angolare
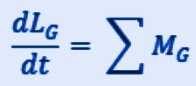
La densità
In generale, quando si studiano i corpi rigidi vengono considerati come corpi continui in cui la massa viene considerata distribuita in modo uniforme all’interno di tutto volume.
la massa totale corrisponde alla somma delle masse infinitesime dm da cui è composto il volume. Con il simbolo 𝛒 viene indicata la densità (o massa volumica), che definisce univocamente la distribuzione di massa nello spazio ed è pari al rapporto tra dm e dV. In particolare diremo che la densità è costante in tutto il volume (𝛒=M/V), quando il corpo è omogeneo.
Il centro di massa corrisponde al centro geometrico del corpo. Ciò vuol dire che un corpo rigido omogeneo che formi un volume dotato di una qualche simmetria, avrà il suo centro di massa nel centro di simmetria del volume occupato.
Possiamo sintetizzare dicendo che in fisica la densità è una grandezza che esprime il rapporto tra la massa di un corpo e il suo volume. Tecnicamente significa quanto segue. La densità indica quanto materiale è contenuto in un certo spazio.
esempi
il ferro ad esempio è un oggetto con alta densità mentre il legno è un oggetto con bassa densità. Gli oggetti con alta densità sono più compatti rispetto a quelli con bassa densità.
Qui di seguito la formula della densità di un corpo:
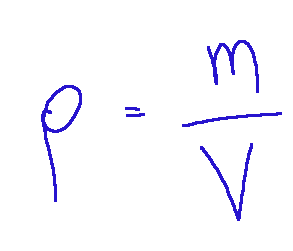
Equilibrio del corpo rigido
Il movimento naturale di un corpo rigido è un moto roto-traslatorio, pertanto la condizione di equilibrio del sistema è data dal fatto che esso non possa né traslare né ruotare.
Dobbiamo tenere presente queste due caratteristiche:
-affinché esso non trasli la somma vettoriale di tutte le forze esterne ad esso applicate deve essere nulla;
-affinché esso non ruoti la somma di tutti i momenti torcenti delle forze ad esso applicati, calcolati rispetto ad un polo qualsiasi, deve essere nulla.
Possiamo dire che il corpo rigido avrà quantità di moto totale e momento angolare costanti.
Possiamo sintetizzare l’equilibrio del corpo rigido dicendo che esso si verifica quando le forze e i momenti applicati su di esso si bilanciano.
Questa condizione particolare impedisce così qualsiasi movimento traslatorio o rotazionale. Gli equilibri possono essere di diverse tipologie. C’è infatti l’equilibrio statico, l’equilibrio dinamico, l’equilibrio traslazione e l’equilibrio rotazionale.
Baricentro di un corpo rigido

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Dopo aver parlato del corpo rigido, del suo equilibrio e della densità, ora parliamo del baricentro di un corpo rigido.
Il baricentro di un corpo rigido è il punto in cui si può considerare concentrata tutta la massa del corpo per facilitare lo studio del suo moto.
Il baricentro è anche il punto in cui la forza peso del corpo agisce come se fosse applicata in un singolo punto.
Il baricentro ha diverse proprietà, qui di seguito ne elenchiamo due:
-Il centro coincide con il centro geometrico se un corpo è omogeneo e ha una forma simmetrica. Un esempio di queste forme possono essere la sfera e il cubo.
-se un corpo ha una distribuzione irregolare della massa, il baricentro dipende dalla disposizione delle diverse parti.
Possiamo dire che il baricentro è fondamentale per studiare l’equilibrio del corpo rigido, perché il corpo tenderà a ruotare intorno a questo punto sotto l’azione delle forze esterne.
Oggi possiamo affermare che calcolare il baricentro di una forma geometrica molto complessa non è poi così difficile in quanto se si riesce a ricreare il modello tridimensionale di questa forma, ci penserà poi il software di modellazione tridimensionale a fornirci il punto esatto in cui si trova il baricentro della massa disegnata.
Conclusioni
In conclusione comprendere bene e studiare i corpi rigidi è importante perché ci permette di semplificare e comprendere meglio il comportamento di oggetti reali nel mondo che ci circonda e per progettare gli oggetti che usiamo quotidianamente.
Domanda
Il concetto di corpo rigido non ha un unico inventore, tuttavia possiamo affermare che nel XVII secolo sono avvenuti degli studi che possiamo definire come i primi studi chiave del concetto moderno del corpo rigido. Lo sapevate che questi studi li aveva fatti proprio Isaac Newton?
THE END